Inhibition of human acid-sensing ion channel 1b by zinc
- PMID: 22837807
- PMCID: PMC3403561
Inhibition of human acid-sensing ion channel 1b by zinc
Abstract
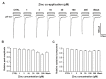
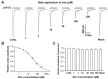
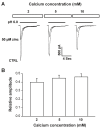
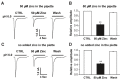
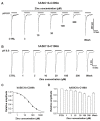
Acid-sensing ion channel 1b (ASIC1b) is expressed in peripheral sensory neurons and has been implicated in nociception. Understanding the modulation of ASIC1b will provide important insight into how ASIC1b contributes to pain sensation. In our previous study, we showed that zinc, an important modulator of pain sensation, reduces rat ASIC1b current. However, rat ASIC1b shows several important differences from its recently identified human homolog. Most noticeably, human ASIC1b (hASIC1b) has a sustained component, which may play a role in persistent pain. Therefore, we tested here the hypothesis that zinc modulates the current properties of hASIC1b. Bath application of zinc suppressed the peak amplitude of hASIC1b currents, with a half-maximum inhibitory concentration of 37 μM. However, zinc did not affect the sustained component of hASIC1b currents. The effect of zinc was independent of pH-dependent activation, steady-state desensitization, and extracellular Ca(2+), suggesting noncompetitive mechanisms. Further, we found that extracellular site(s) of the hASIC1b subunit is important for the effect of zinc. Mutating cysteine 196, but not cysteine 309, in the extracellular domain of the hASIC1b abolished the zinc inhibition. These results suggest that, through modulating cysteine196, zinc may have a modulatory role in acute pain.
Keywords: Acid-sensing ion channels; hASIC1b; pain; patch-clamp; zinc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cysteine 149 in the extracellular finger domain of acid-sensing ion channel 1b subunit is critical for zinc-mediated inhibition.Neuroscience. 2011 Oct 13;193:89-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.021. Epub 2011 Jul 14. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21767613 Free PMC article.
-
Two PKC consensus sites on human acid-sensing ion channel 1b differentially regulate its function.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009 Feb;296(2):C372-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00200.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19091960 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1b in the Development of Acid-Induced Chronic Muscle Pain.Front Neurosci. 2019 Nov 22;13:1247. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01247. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31824248 Free PMC article.
-
ASIC3 channels in multimodal sensory perception.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011 Jan 19;2(1):26-37. doi: 10.1021/cn100094b. Epub 2010 Nov 12. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22778854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptides inhibitors of acid-sensing ion channels.Toxicon. 2007 Feb;49(2):271-84. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.09.026. Epub 2006 Oct 4. Toxicon. 2007. PMID: 17113616 Review.
Cited by
-
The diverse functions of the DEG/ENaC family: linking genetic and physiological insights.J Physiol. 2023 May;601(9):1521-1542. doi: 10.1113/JP283335. Epub 2022 Nov 13. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36314992 Free PMC article.
-
The direct modulatory activity of zinc toward ion channels.Integr Med Res. 2015 Sep;4(3):142-146. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2015.07.004. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Integr Med Res. 2015. PMID: 28664120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of Zinc Homeostasis for Normal Cardiac Rhythm.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2025;21(2):e1573403X299868. doi: 10.2174/011573403X299868240904120621. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39301907 Review.
-
Knockdown of acid-sensing ion channel 1a (ASIC1a) suppresses disease phenotype in SCA1 mouse model.Cerebellum. 2014 Aug;13(4):479-90. doi: 10.1007/s12311-014-0563-6. Cerebellum. 2014. PMID: 24788087
-
Acid-sensing ion channels: trafficking and synaptic function.Mol Brain. 2013 Jan 2;6:1. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-6-1. Mol Brain. 2013. PMID: 23281934 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kellenberger S, Schild L. Epithelial sodium channel/degenerin family of ion channels: a variety of functions for a shared structure. Physiol Review. 2002;82:735–767. - PubMed
-
- Krishtal O. The ASICs: signaling moleculars? modulators? Trends Neurosci. 2003;26:477–483. - PubMed
-
- Wemmie JA, Price MP, Welsh MJ. Acidsensing ion channels: advances, questions and therapeutic opportunities. Trends Neurosci. 2006;29:578–586. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
