Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous tooth-derived conditioned medium enhance recovery of focal cerebral ischemia in rats
- PMID: 22839964
- PMCID: PMC3530935
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2011.0385
Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous tooth-derived conditioned medium enhance recovery of focal cerebral ischemia in rats
Abstract
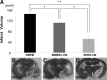
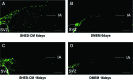
Regenerative therapy using stem cells is a promising approach for the treatment of stroke. Recently, we reported that dental pulp stem cells (DPSC) ameliorated ischemic tissue injury in the rat brain and accelerated functional recovery after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). In this study, we investigated the effects of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous tooth (SHED)-derived conditioned medium (SHED-CM) on permanent MCAO (pMCAO). Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to pMCAO. SHED-CM were then administered intranasally, and the motor function and infarct volume were evaluated. Neurogenesis and vasculogenesis were determined using immunochemical markers. The SHED-CM group had more positive signals than the Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium group, with doublecortin (DCX), neurofilament H, neuronal nuclei, and rat endothelial cell antigen observed in the peri-infarct area. Migration of neuronal progenitor cells (NPC) with DCX from the subventricular zone to the peri-infarct area was observed on days 6 and 16, with migration on day 6 being the most prominent. In conclusion, SHED-CM promoted the migration and differentiation of endogenous NPC, induced vasculogenesis, and ameliorated ischemic brain injury after pMCAO as well as transplantation of DPSC.
Figures



References
-
- Donnan G.A. Fisher M. Macleod M. Davis S.M. Stroke. Lancet. 2008;371:1612. - PubMed
-
- Bang O.Y. Lee J.S. Lee P.H. Lee G. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in stroke patients. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:874. - PubMed
-
- Kern S. Eichler H. Stoeve J. Klüter H. Bieback K. Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 2006;24:1294. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura S. Yamada Y. Katagiri W. Sugito T. Ito K. Ueda M. Stem cell proliferation pathways comparison between human exfoliated deciduous teeth and dental pulp stem cells by gene expression profile from promising dental pulp. J Endod. 2009;35:1536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

