The Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2): study design and baseline characteristics (AREDS2 report number 1)
- PMID: 22840421
- PMCID: PMC3485447
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.05.027
The Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2): study design and baseline characteristics (AREDS2 report number 1)
Abstract
Purpose: The Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS) demonstrated beneficial effects of oral supplementation with antioxidant vitamins and minerals on the development of advanced age-related macular degeneration (AMD) in persons with at least intermediate AMD (bilateral large drusen with or without pigment changes). Observational data suggest that other oral nutrient supplements might further reduce the risk of progression to advanced AMD. The primary purpose of the Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2) is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of lutein plus zeaxanthin (L+Z) and/or ω-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (LCPUFA) supplementation in reducing the risk of developing advanced AMD. The study also assesses the reduction in zinc and the omission of β-carotene from original AREDS formulation.
Design: Multicenter, phase III, randomized, controlled clinical trial.
Participants: Persons aged 50 to 85 with bilateral intermediate AMD or advanced AMD in 1 eye.
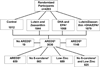
Methods: All participants were randomly assigned to placebo (n = 1012), L+Z (10 mg/2 mg; n = 1044), ω-3 LCPUFAs (eicosapentaenoic acid + docosahexaenoic acid [650 mg/350 mg]; n = 1069), or the combination of L+Z and ω-3 LCPUFAs (n = 1078). All participants were offered a secondary randomization to 1 of 4 variations of the original AREDS formulation keeping vitamins C (500 mg) and E (400 IU) and copper (2 mg) unchanged while varying zinc and β-carotene as follows: Zinc remains at the original level (80 mg), lower only zinc to 25 mg, omit β-carotene only, or lower zinc to 25 mg and omit β-carotene.
Main outcome measures: Progression to advanced AMD determined by centralized grading of annual fundus photographs.
Results: We enrolled 4203 participants at 82 clinical centers located in the United States. Population characteristics at baseline were as follows: Mean age, 74 years; 57% female; 97% white; 7% current smokers; 19% with prior cardiovascular disease; and 44% and 50% taking statin-class cholesterol-lowering drugs and aspirin, respectively. Ocular characteristics include 59% with bilateral large drusen, 32% with advanced AMD in 1 eye and mean visual acuity of 20/32 in eyes without advanced AMD.
Conclusions: This report presents the AREDS2 study design and the participants' baseline demographic and ocular characteristics.
Copyright © 2012 American Academy of Ophthalmology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial Interest: A complete list of all AREDS2 investigator financial disclosures, which were collected for regulatory purposes, pursuant to US FDA regulations in 21 CFR Part 54, can be found at
Figures
References
-
- Eye Diseases Prevalence Research Group. Causes and prevalence of visual impairment among adults in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122:477–485. - PubMed
-
- Eye Diseases Prevalence Research Group. Prevalence of age-related macular degeneration in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122:564–572. - PubMed
-
- Goldman HB, Kiffel S, Weinstock FJ. Cataract surgery and the primary care practitioner. Geriatrics. 2009;64:19–22. 25–26. - PubMed
-
- Eye Diseases Prevalence Research Group. Prevalence of cataract and pseudophakia/aphakia among adults in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122:487–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

