DNA sequence preferences of transcriptional activators correlate more strongly than repressors with nucleosomes
- PMID: 22841002
- PMCID: PMC3566590
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.06.028
DNA sequence preferences of transcriptional activators correlate more strongly than repressors with nucleosomes
Abstract
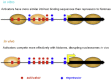
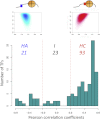
Transcription factors (TFs) and histone octamers are two abundant classes of DNA binding proteins that coordinate the transcriptional program in cells. Detailed studies of individual TFs have shown that TFs bind to nucleosome-occluded DNA sequences and induce nucleosome disruption/repositioning, while recent global studies suggest this is not the only mechanism used by all TFs. We have analyzed to what extent the intrinsic DNA binding preferences of TFs and histones play a role in determining nucleosome occupancy, in addition to nonintrinsic factors such as the enzymatic activity of chromatin remodelers. The majority of TFs in budding yeast have an intrinsic sequence preference overlapping with nucleosomal histones. TFs with intrinsic DNA binding properties highly correlated with those of histones tend to be associated with gene activation and might compete with histones to bind to genomic DNA. Consistent with this, we show that activators induce more nucleosome disruption upon transcriptional activation than repressors.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Badis G., Chan E.T., van Bakel H., Pena-Castillo L., Tillo D., Tsui K., Carlson C.D., Gossett A.J., Hasinoff M.J., Warren C.L. A library of yeast transcription factor motifs reveals a widespread function for Rsc3 in targeting nucleosome exclusion at promoters. Mol. Cell. 2008;32:878–887. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bryant G.O., Ptashne M. Independent recruitment in vivo by Gal4 of two complexes required for transcription. Mol. Cell. 2003;11:1301–1309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

