Repetitive electroacupuncture causes prolonged increased met-enkephalin expression in the rVLM of conscious rats
- PMID: 22841685
- PMCID: PMC3461830
- DOI: 10.1016/j.autneu.2012.07.001
Repetitive electroacupuncture causes prolonged increased met-enkephalin expression in the rVLM of conscious rats
Abstract
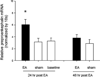
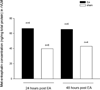
Enkephalinergic neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla (rVLM), an important presympathetic region in the brainstem, are activated by 30 min of low frequency (2 Hz) electroacupuncture (EA) at acupoints P5-P6, which overlie the median nerves. To more closely model the clinical application of acupuncture, we administered EA for 30 min twice over a 72 h period to unsedated conscious rats to examine its prolonged action. We hypothesized that repetitive EA would increase preproenkephalin mRNA and met-enkephalin in the rVLM of unsedated conscious rats. Rats received either EA (1-4 mA, 0.5 ms, 2 Hz) or sham stimulation (needle placement without electrical stimulation) twice at P5-P6 acupoints bilaterally. Preproenkephalin mRNA and its peptide met-enkephalin in the rVLM were measured 24 or 48 h after the final EA or sham procedure. Relative ratios of preproenkephalin mRNA levels (normalized with the 18S housekeeping gene) were almost doubled at 24h compared to sham (6.1 ± 0.79 vs. 3.1 ± 0.47). Met-enkephalin measured in rVLM tissue pooled from several rats exposed to the same treatment was increased by repeated EA by 68% after 24h and 51% after 48h, relative to sham. These findings suggest that repeated application of EA in the conscious rats enhances transcription and translation of enkephalin in rVLM for days. Since opioids in the rVLM contribute importantly to the action of EA on sympathetic outflow, this mechanism may contribute to the prolonged action of acupuncture on elevated blood pressure in patients.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Almeida OF, Hassan AH, Harbuz MS, Linton EA, Lightman SL. Hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone and opioid peptide neurons: functional changes after adrenalectomy and/or castration. Brain Res. 1992;571:189–198. - PubMed
-
- Andersson The functional background in acupuncture effects. Scand.J.Rehabil.Med.Suppl. 1993;29:31–60. - PubMed
-
- Chao DM, Shen LL, Tjen-A-Looi SC, Pitsillides KF, Li P, Longhurst JC. Naloxone reverses inhibitory effect of electroacupuncture on sympathetic cardiovascular reflex responses. Am.J.Physiol. 1999;276:H2127–H2134. - PubMed
-
- Chiu YJ, Chi A, Reid IA. Cardiovascular and endocrine effects of acupuncture in hypertensive patients. Clin.Exp.Hyperten. 1997;19:1047–1063. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

