Nuclear depletion of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (Ape1/Ref-1) is an indicator of energy disruption in neurons
- PMID: 22841870
- PMCID: PMC3487712
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.07.025
Nuclear depletion of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (Ape1/Ref-1) is an indicator of energy disruption in neurons
Abstract
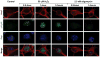
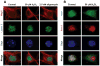
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (Ape1/Ref-1) is a multifunctional protein critical for cellular survival. Its involvement in adaptive survival responses includes key roles in redox sensing, transcriptional regulation, and repair of DNA damage via the base excision repair (BER) pathway. Ape1 is abundant in most cell types and central in integrating the first BER step catalyzed by different DNA glycosylases. BER is the main process for removal of oxidative DNA lesions in postmitotic brain cells, and after ischemic brain injury preservation of Ape1 coincides with neuronal survival, while its loss has been associated with neuronal death. Here, we report that in cultured primary neurons, diminution of cellular ATP by either oligomycin or H(2)O(2) is accompanied by depletion of nuclear Ape1, while other BER proteins are unaffected and retain their nuclear localization under these conditions. Importantly, while H(2)O(2) induces γH2AX phosphorylation, indicative of chromatin rearrangements in response to DNA damage, oligomycin does not. Furthermore, despite comparable diminution of ATP content, H(2)O(2) and oligomycin differentially affect critical parameters of mitochondrial respiration that ultimately determine cellular ATP content. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that in neurons, nuclear compartmentalization of Ape1 depends on ATP and loss of nuclear Ape1 reflects disruption of neuronal energy homeostasis. Energy crisis is a hallmark of stroke and other ischemic/hypoxic brain injuries. In vivo studies have shown that Ape1 deficit precedes neuronal loss in injured brain regions. Thus, our findings bring to light the possibility that energy failure-induced Ape1 depletion triggers neuronal death in ischemic brain injuries.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Oxidative DNA damage is concurrently repaired by base excision repair (BER) and apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1)-initiated nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) in cortical neurons.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2020 Jun;46(4):375-390. doi: 10.1111/nan.12584. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31628877 Free PMC article.
-
Human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 is modified in vitro by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 under control of the structure of damaged DNA.Biochimie. 2020 Jan;168:144-155. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2019.10.011. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Biochimie. 2020. PMID: 31668992
-
The role of the N-terminal domain of human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1, APE1, in DNA glycosylase stimulation.DNA Repair (Amst). 2018 Apr;64:10-25. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.02.001. Epub 2018 Feb 11. DNA Repair (Amst). 2018. PMID: 29475157
-
Inhibitors of nuclease and redox activity of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox effector factor 1 (APE1/Ref-1).Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 May 1;25(9):2531-2544. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.01.028. Epub 2017 Jan 21. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28161249 Review.
-
APE1/Ref-1 as an emerging therapeutic target for various human diseases: phytochemical modulation of its functions.Exp Mol Med. 2014 Jul 18;46(7):e106. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.42. Exp Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 25033834 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cisplatin Toxicity in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons Is Relieved by Meclizine via Diminution of Mitochondrial Compromise and Improved Clearance of DNA Damage.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Dec;54(10):7883-7895. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0273-9. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27858292 Free PMC article.
-
APE1, the DNA base excision repair protein, regulates the removal of platinum adducts in sensory neuronal cultures by NER.Mutat Res. 2015 Sep;779:96-104. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2015.06.010. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Mutat Res. 2015. PMID: 26164266 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress stimulates invasive potential in rat C6 and human U-87 MG glioblastoma cells via activation and cross-talk between PKM2, ENPP2 and APE1 enzymes.Metab Brain Dis. 2018 Aug;33(4):1307-1326. doi: 10.1007/s11011-018-0233-3. Epub 2018 May 2. Metab Brain Dis. 2018. PMID: 29721771
-
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 upregulation reduces oxidative DNA damage and protects hippocampal neurons from ischemic injury.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015 Jan 10;22(2):135-48. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5511. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015. PMID: 24180454 Free PMC article.
-
MSC-Based Cell Therapy in Neurological Diseases: A Concise Review of the Literature in Pre-Clinical and Clinical Research.Biomolecules. 2024 Apr 30;14(5):538. doi: 10.3390/biom14050538. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38785945 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fishel ML, Kelley MR. The DNA base excision repair protein Ape1/Ref-1 as a therapeutic and chemopreventive target. Mol Aspects Med. 2007;28:375–395. - PubMed
-
- Ludwig DL, MacInnes MA, Takiguchi Y, Purtymun PE, Henrie M, Flannery M, Meneses J, Pedersen RA, Chen DJ. A murine AP-endonuclease gene-targeted deficiency with post-implantation embryonic progression and ionizing radiation sensitivity. Mutat Res. 1998;409:17–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

