Interferon-inducible Ifi200-family genes as modifiers of lupus susceptibility
- PMID: 22841963
- PMCID: PMC3425670
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imlet.2012.07.003
Interferon-inducible Ifi200-family genes as modifiers of lupus susceptibility
Abstract
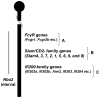
Both genetic and environmental factors contribute to the development and progression of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a complex autoimmune disease. The disease exhibits a strong gender bias and develops predominantly in females. Additionally, most SLE patients exhibit increased serum levels of interferon-α (IFN-α) and the "IFN signature". Studies using the mouse models of lupus have identified several lupus susceptibility loci, including the New Zealand Black (NZB)-derived autoimmunity 2 (Nba2) interval on the chromosome 1. The interval, which is syntenic to the human chromosome 1q region, harbors the FcγR family, SLAM/CD2-family, and the IFN-inducible Ifi200-family genes (encoding for the p200-family proteins). Studies involving the B6.Nba2 congenic mice revealed that the development of antinuclear autoantibodies (ANAs) depends on the age, gender, and activation of type I IFN-signaling. Interestingly, recent studies involving the generation of Nba2 subcongenic mouse lines and generation of mice deficient for the Fcgr2b or Aim2 gene within the interval have provided evidence that epistatic interactions among the Nba2 genes contribute to increased lupus susceptibility. Given that the expression of some of the p200-family proteins is differentially regulated by sex hormones and these proteins differentially regulate cytosolic DNA-induced production of type I IFN and proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and IL-18), the major known contributors of SLE-associated inflammation, we discuss the recent advancements in our understanding of the role of p200-family proteins in lupus susceptibility modification. An improved understanding of the role of p200-family proteins in the development of autoimmunity is likely to identify new approaches to treat SLE patients.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

