Hydroxyapatite nanoparticle reinforced peptide amphiphile nanomatrix enhances the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by compositional ratios
- PMID: 22842043
- PMCID: PMC3462224
- DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.07.024
Hydroxyapatite nanoparticle reinforced peptide amphiphile nanomatrix enhances the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by compositional ratios
Abstract
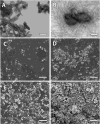
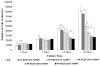
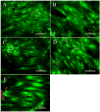
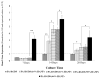
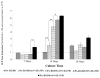
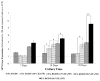
In the field of bone tissue engineering, there is a need for materials that mimic the native bone extracellular matrix (ECM). This need is met through the creation of biphasic composites intended to mimic both the organic and inorganic facets of the native bone ECM. However, few studies have created composites with organic ECM analogous components capable of directing cellular behaviors and many are not fabricated in the nanoscale. Furthermore, few attempts have been made at investigating how variations of organic and inorganic components affect the osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). To address these issues, biphasic nanomatrix composites consisting of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (HANPs) embedded within peptide amphiphile (PA) nanofibers tailored with the RGDS cellular adhesion motif (PA-RGDS) were created at various HANP to PA-RGDS ratios. Fabrication of these biphasic nanomatrix composites was confirmed via scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The long-term cellularity and osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs in response to the different compositional ratios were then assessed by quantifying the timed expression of genes indicative of osteogenic differentiation, alkaline phosphatase activity, and DNA content over time. Decreased cellularity and the expression of genes over time correlated with increasing compositional ratios between HANP and PA-RGDS. The highest HANP to PA-RGDS ratio (66% HANP) exhibited the greatest improvement to the osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs. Overall, these results demonstrate that the compositional ratio of biphasic nanomatrix composites plays an important role in influencing the osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs. Based on the observations presented within this study, these biphasic nanomatrix composites show promise for future usage in bone tissue engineering applications.
Copyright © 2012 Acta Materialia Inc. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

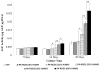
Similar articles
-
Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells synergistically enhanced by biomimetic peptide amphiphiles combined with conditioned medium.Acta Biomater. 2011 Feb;7(2):675-82. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2010.08.016. Epub 2010 Aug 20. Acta Biomater. 2011. PMID: 20728586 Free PMC article.
-
Biphasic peptide amphiphile nanomatrix embedded with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for stimulated osteoinductive response.ACS Nano. 2011 Dec 27;5(12):9463-79. doi: 10.1021/nn203247m. Epub 2011 Nov 17. ACS Nano. 2011. PMID: 22077993 Free PMC article.
-
Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells directed by extracellular matrix-mimicking ligands in a biomimetic self-assembled peptide amphiphile nanomatrix.Biomacromolecules. 2009 Oct 12;10(10):2935-44. doi: 10.1021/bm9007452. Biomacromolecules. 2009. PMID: 19746964 Free PMC article.
-
Mineralization of peptide amphiphile nanofibers and its effect on the differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells.Acta Biomater. 2012 Jul;8(7):2456-65. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.03.026. Epub 2012 Mar 19. Acta Biomater. 2012. PMID: 22440242 Free PMC article.
-
Nano-Hydroxyapatite Coating Promotes Porous Calcium Phosphate Ceramic-Induced Osteogenesis Via BMP/Smad Signaling Pathway.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Oct 3;14:7987-8000. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S216182. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31632013 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Research trends in biomimetic medical materials for tissue engineering: 3D bioprinting, surface modification, nano/micro-technology and clinical aspects in tissue engineering of cartilage and bone.Biomater Res. 2016 May 4;20:10. doi: 10.1186/s40824-016-0057-3. eCollection 2016. Biomater Res. 2016. PMID: 27148455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incorporating strontium enriched amorphous calcium phosphate granules in collagen/collagen-magnesium-hydroxyapatite osteochondral scaffolds improves subchondral bone repair.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Jan 20;25:100959. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.100959. eCollection 2024 Apr. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 38327976 Free PMC article.
-
Titanium Dental Implants: An Overview of Applied Nanobiotechnology to Improve Biocompatibility and Prevent Infections.Materials (Basel). 2022 Apr 27;15(9):3150. doi: 10.3390/ma15093150. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35591484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fabrication and Characterization of Silk Fibroin Microfiber-Incorporated Bone Marrow Stem Cell Spheroids to Promote Cell-Cell Interaction and Osteogenesis.ACS Omega. 2020 Jul 16;5(29):18021-18027. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c01415. eCollection 2020 Jul 28. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32743175 Free PMC article.
-
Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Stem Cell in Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) Scaffold Loaded Various Ratio of Hydroxyapatite.Int J Stem Cells. 2013 May;6(1):67-74. doi: 10.15283/ijsc.2013.6.1.67. Int J Stem Cells. 2013. PMID: 24298375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashman RF, Buckwalter JA, Devane P, Dobbs MB, Ferguson PJ, Flatow EL, et al. Turek’s Orthopaedics: Principles and Their Application. 6. Iowa City: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2005.
-
- Bonzani IC, George JH, Stevens MM. Novel materials for bone and cartilage regeneration. Current opinion in chemical biology. 2006;10:568–75. - PubMed
-
- Couchman JR, Austria MR, Woods A. Fibronectin-cell interactions. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 1990;94:7S–14S. - PubMed
-
- Hartgerink JD, Beniash E, Stupp SI. Self-assembly and mineralization of peptide-amphiphile nanofibers. Science. 2001;294:1684–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

