MDMA produces a delayed and sustained increase in the extracellular concentration of glutamate in the rat hippocampus
- PMID: 22842073
- PMCID: PMC3437747
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.07.026
MDMA produces a delayed and sustained increase in the extracellular concentration of glutamate in the rat hippocampus
Abstract
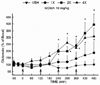
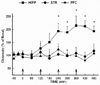
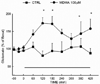
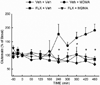
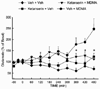
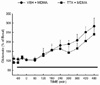
The neurochemical effects of MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine) on monoaminergic and cholinergic systems in the rat brain have been well documented. However, little is known regarding the effects of MDMA on glutamatergic systems in the brain. In the present study the effects of multiple injections of MDMA on extracellular concentrations of glutamate in the striatum, prefrontal cortex, and dorsal hippocampus were examined. Two or four, but not one, injections of MDMA (10 mg/kg, i.p. at 2 h intervals) resulted in a 2-3 fold increase in the extracellular concentration of glutamate in the hippocampus; no increase was evident in the striatum or prefrontal cortex. Reverse dialysis of MDMA (100 μM) into the hippocampus also elicited an increase in extracellular glutamate. Treatment with the 5-HT reuptake inhibitor fluoxetine prevented the increase in extracellular glutamate in the hippocampus following the systemic administration of MDMA, as did treatment with the serotonin 5-HT2A/C receptor antagonist ketanserin. Moreover, reverse dialysis of the sodium channel blocker tetrodotoxin did not prevent the increase in extracellular glutamate in the hippocampus. These data support the view that stimulation of 5-HT2A/2C receptors on non-neuronal cells by 5-HT released by MDMA promotes glutamate efflux in the hippocampus.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Adori C, Ando RD, Balazsa T, Soti C, Vas S, Palkovits M, Kovacs GG, Bagdy G. Low ambient temperature reveals distinct mechanisms for MDMA-induced serotonergic toxicity and astroglial Hsp27 heat shock response in rat brain. Neurochemistry International. 2011;59:695–705. - PubMed
-
- Appel NM, Mitchell WM, Garlick RK, Glennon RA, Teitler M, De Souza EB. Autoradiographic characterization of (+-)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-[125I] iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane ([125I]DOI) binding to 5-HT2 and 5-HT1c receptors in rat brain. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1990;255:843–857. - PubMed
-
- Capela JP, Ruscher K, Lautenschlager M, Freyer D, Dirnagl U, Gaio AR, Bastos ML, Meisel A, Carvalho F. Ecstasy-induced cell death in cortical neuronal cultures is serotonin 2A-receptor-dependent and potentiated under hyperthermia. Neuroscience. 2006;139:1069–1081. - PubMed
-
- Cornea-Hebert V, Riad M, Wu C, Singh SK, Descarries L. Cellular and subcellular distribution of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor in the central nervous system of adult rat. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1999;409:187–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

