NMNAT1 mutations cause Leber congenital amaurosis
- PMID: 22842227
- PMCID: PMC3454532
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2361
NMNAT1 mutations cause Leber congenital amaurosis
Abstract
Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA) is an infantile-onset form of inherited retinal degeneration characterized by severe vision loss(1,2). Two-thirds of LCA cases are caused by mutations in 17 known disease-associated genes(3) (Retinal Information Network (RetNet)). Using exome sequencing we identified a homozygous missense mutation (c.25G>A, p.Val9Met) in NMNAT1 that is likely to be disease causing in two siblings of a consanguineous Pakistani kindred affected by LCA. This mutation segregated with disease in the kindred, including in three other children with LCA. NMNAT1 resides in the previously identified LCA9 locus and encodes the nuclear isoform of nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase, a rate-limiting enzyme in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD(+)) biosynthesis(4,5). Functional studies showed that the p.Val9Met alteration decreased NMNAT1 enzyme activity. Sequencing NMNAT1 in 284 unrelated families with LCA identified 14 rare mutations in 13 additional affected individuals. These results are the first to link an NMNAT isoform to disease in humans and indicate that NMNAT1 mutations cause LCA.
Figures

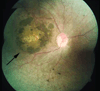
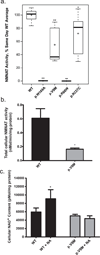
Comment in
-
Novel NMNAT1 mutations causing Leber congenital amaurosis identified.Clin Genet. 2013 Jan;83(1):33-4. doi: 10.1111/cge.12043. Clin Genet. 2013. PMID: 23088368 No abstract available.
References
-
- Weleber RG. Infantile and childhood retinal blindness: a molecular perspective. Ophthalmic Genet. 2002:71–97. - PubMed
-
- Michaelides M, Hardcastle AJ, Hunt DM, Moore AT. Progressive cone and cone-rod dystrophies: phenotypes and underlying molecular genetic basis. Survey of Ophthalmology. 2006;51:232–258. - PubMed
-
- Keen TJ, et al. Identification of a locus (LCA9) for Leber's congenital amaurosis on chromosome 1p36. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2003;11:420–423. - PubMed
-
- Lau C, Niere M, Ziegler M. The NMN/NaMN adenylyltransferase (NMNAT) protein family. Front. Biosci. 2009;14:410–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30EY014104/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK082521/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03-DK082446/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-EY12910/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD026979/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01-GM097409/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30HD026979/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD065858/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY012910/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM097409/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY014104/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

