OX40 signaling favors the induction of T(H)9 cells and airway inflammation
- PMID: 22842344
- PMCID: PMC3806044
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2390
OX40 signaling favors the induction of T(H)9 cells and airway inflammation
Abstract
The mechanisms that regulate the T(H)9 subset of helper T cells and diseases mediated by T(H)9 cells remain poorly defined. Here we found that the costimulatory receptor OX40 was a powerful inducer of T(H)9 cells in vitro and T(H)9 cell-dependent airway inflammation in vivo. In polarizing conditions based on transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), ligation of OX40 inhibited the production of induced regulatory T cells and the T(H)17 subset of helper T cells and diverted CD4(+)Foxp3(-) T cells to a T(H)9 phenotype. Mechanistically, OX40 activated the ubiquitin ligase TRAF6, which triggered induction of the kinase NIK in CD4(+) T cells and the noncanonical transcription factor NF-κB pathway; this subsequently led to the generation of T(H)9 cells. Thus, our study identifies a previously unknown mechanism for the induction of T(H)9 cells and may have important clinical implications in allergic inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures


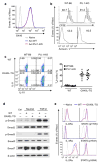


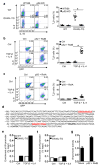


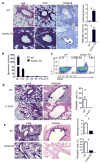
Comment in
-
Yoking OX40 to regulation of IL-9.Nat Immunol. 2012 Oct;13(10):942-3. doi: 10.1038/ni.2421. Nat Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22990899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Janeway CA, Bottomly K. Signals and signs for lymphocyte responses. Cell. 1994;76:275–285. - PubMed
-
- Li XC, Rothstein DM, Sayegh MH. Costimulatory pathways in transplantation: challenges and new developments. Immunological Reviews. 2009;229:271–293. - PubMed
-
- Dong C. Diversification of T helper cell lineages: finding the family root of IL-17-producing cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:329–334. - PubMed
-
- Bettelli E, et al. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector Th17 and regulatory cells. Nature. 2006;441:235–238. - PubMed
-
- Staudt V, et al. Interferon-regulatory factor 4 is essential for the developmental program of T helper 9 cells. Immunity. 2010;33:192–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

