Cone beam CT image artefacts related to head motion simulated by a robot skull: visual characteristics and impact on image quality
- PMID: 22842641
- PMCID: PMC3699011
- DOI: 10.1259/dmfr/32310645
Cone beam CT image artefacts related to head motion simulated by a robot skull: visual characteristics and impact on image quality
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to assess artefacts and their impact on cone beam CT (CBCT) image quality (IQ) after head motion simulated by a robot skull.
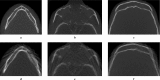
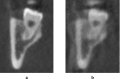
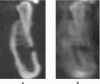
Methods: A fully dentate human skull incorporated into a robot simulated pre-determined patient movements. Ten head motion patterns were selected based on the movement of the C-arm of the CBCT units (no motion as reference). Three CBCT units were used [a three-dimensional eXam (K) (KaVo Dental GmbH, Biberach, Germany), a Promax 3D MAX (P) (Planmeca Oy, Helsinki, Finland) and a Scanora(®) 3D (S) (Soredex Oy, Tuusula, Finland)]. Axial images were qualitatively assessed at three levels: mental foramen (MF), infraorbital foramen and supraorbital foramen, and artefacts characterized as stripe-like, double contours, unsharpness or ring-like. A 100 mm visual analogue scale (VAS) was used to quantitatively assess IQ. Cross-sectional images of the lower third molar and MF bilaterally were also evaluated by VAS. Four blinded examiners assessed the images.
Results: For all units and motion patterns, stripe-like artefacts were the most common. The four observers agreed on the presence of at least one artefact type in 90% of the images. Axial images showed lower overall IQ after motion (VAS = 72.4 ± 24.0 mm) than reference images (VAS = 97.3 ± 2.6 mm). The most severe artefacts were seen at the MF level. For cross-sectional images, IQ was lowest after tremor. The mean IQ range was 74-89 and 57-90 for isolated (tilting, rotation and nodding) and combined (nodding + tilting and rotation + tilting) movements, respectively. IQ for MF was lower than for third molar for any movement except tremor.
Conclusions: Head motion of any type resulted in artefacts in CBCT images. The impact on IQ depended on the region and level in the skull.
Figures
References
-
- Hanzelka T, Foltan R, Horka E, Sedy J. Reduction of the negative influence of patient motion on quality of CBCT scan. Med Hypotheses 2010; 75: 610–612 - PubMed
-
- Draenert FG, Coppenrath E, Herzog P, Muller S, Mueller-Lisse UG. Beam hardening artefacts occur in dental implant scans with the NewTom cone beam CT but not with the dental 4-row multidetector CT. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2007; 36: 198–203 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

