The neural correlates of positive self-evaluation and self-related memory
- PMID: 22842813
- PMCID: PMC3831555
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nss086
The neural correlates of positive self-evaluation and self-related memory
Abstract
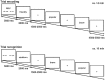
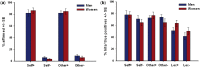
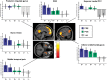
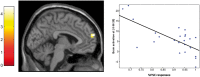
Humans tend to have a positive self-evaluation (PSE). To what extent positive self-perception is interacting with valenced self-related memories is debated. The underlying neural substrates are not adequately explained yet. To explore the cerebral correlates of PSE and its influence on memory, 24 healthy subjects were asked during fMRI to decide in two conditions whether presented positive and negative personality traits characterized their own selves (self-evaluation) or an intimate other (other-evaluation). A lexical condition served as control task. In a subsequent unannounced recognition task, trait adjectives had to be classified as old or new. Activation during positive self- vs positive other-evaluation was found in the medial ventral and dorsolateral prefrontal gyri, the parahippocampus and the supplementary motor area. Memory increased for positive personality traits and traits that had been referred to oneself or the other. In contrast to adjectives of the other-evaluation or lexical condition, recollection of negative vs positive traits of the self-evaluation condition specifically induced increased activation in the hippocampus and several prefrontal and temporal areas. Our data imply a specific network for PSE (although intimate others are perceived similarly). Moreover, memory for traits contradicting PSE resulted in activation increases indicating greater cognitive effort and emotional involvement.
Keywords: emotion; fMRI; memory; recognition; self.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distributed self in episodic memory: neural correlates of successful retrieval of self-encoded positive and negative personality traits.Neuroimage. 2004 Aug;22(4):1596-604. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.03.034. Neuroimage. 2004. PMID: 15275916
-
In search of the emotional self: an fMRI study using positive and negative emotional words.Am J Psychiatry. 2003 Nov;160(11):1938-45. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.160.11.1938. Am J Psychiatry. 2003. PMID: 14594739
-
Don't worry, be happy - Neural correlates of the influence of musically induced mood on self-evaluation.Neuropsychologia. 2017 Jun;100:26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.04.010. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Neuropsychologia. 2017. PMID: 28392302
-
Differential remoteness and emotional tone modulate the neural correlates of autobiographical memory.Brain. 2003 Mar;126(Pt 3):650-68. doi: 10.1093/brain/awg064. Brain. 2003. PMID: 12566286
-
Cognitive and neuroimaging evidence of impaired interaction between self and memory in Alzheimer's disease.Cortex. 2014 Feb;51:11-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2013.06.009. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Cortex. 2014. PMID: 23993283
Cited by
-
Me, myself and I: temporal dysfunctions during self-evaluation in patients with schizophrenia.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2014 Nov;9(11):1779-88. doi: 10.1093/scan/nst174. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24369435 Free PMC article.
-
Coping with Self-Threat and the Evaluation of Self-Related Traits: An fMRI Study.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 2;10(9):e0136027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136027. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26333130 Free PMC article.
-
Self-referential encoding of source information in recollection memory.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 15;16(4):e0248044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248044. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33857141 Free PMC article.
-
The neural basis of trait self-esteem revealed by the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations and resting state functional connectivity.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016 Mar;11(3):367-76. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsv119. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26400859 Free PMC article.
-
The Neural Correlates of Optimistic and Depressive Tendencies of Self-Evaluations and Resting-State Default Mode Network.Front Hum Neurosci. 2015 Nov 18;9:618. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00618. eCollection 2015. Front Hum Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26635573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham A, Schubotz RI, von Cramon DY. Thinking about the future versus the past in personal and non-personal contexts. Brain Research. 2008;1233:106–19. - PubMed
-
- Amodio DM, Frith CD. Meeting of minds: the medial frontal cortex and social cognition. Nature. 2006;7:268–77. - PubMed
-
- Beer JS, Hughes BL. Neural systems of social comparison and the “above-average” effect. NeuroImage. 2010;49:2671–9. - PubMed
-
- Benoit RG, Gilbert SJ, Volle E, Burgess PW. When I think about me and simulate you: medial rostral prefrontal cortex and self-referential processes. NeuroImage. 2010;50:1340–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

