Peroxidasin forms sulfilimine chemical bonds using hypohalous acids in tissue genesis
- PMID: 22842973
- PMCID: PMC4128002
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1038
Peroxidasin forms sulfilimine chemical bonds using hypohalous acids in tissue genesis
Abstract
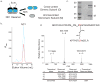
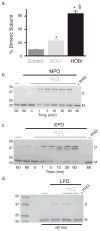
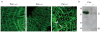
Collagen IV comprises the predominant protein network of basement membranes, a specialized extracellular matrix, which underlie epithelia and endothelia. These networks assemble through oligomerization and covalent crosslinking to endow mechanical strength and shape cell behavior through interactions with cell-surface receptors. A recently discovered sulfilimine (S=N) bond between a methionine sulfur and hydroxylysine nitrogen reinforces the collagen IV network. We demonstrate that peroxidasin, an enzyme found in basement membranes, catalyzes formation of the sulfilimine bond. Drosophila peroxidasin mutants have disorganized collagen IV networks and torn visceral muscle basement membranes, pointing to a critical role for the enzyme in tissue biogenesis. Peroxidasin generates hypohalous acids as reaction intermediates, suggesting a paradoxically anabolic role for these usually destructive oxidants. This work highlights sulfilimine bond formation as what is to our knowledge the first known physiologic function for peroxidasin, a role for hypohalous oxidants in tissue biogenesis, and a possible role for peroxidasin in inflammatory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Poschl E, et al. Collagen IV is essential for basement membrane stability but dispensable for initiation of its assembly during early development. Development. 2004;131:1619–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

