Targeting αV-integrins decreased metastasis and increased survival in a nude rat breast cancer brain metastasis model
- PMID: 22842979
- PMCID: PMC3726254
- DOI: 10.1007/s11060-012-0942-0
Targeting αV-integrins decreased metastasis and increased survival in a nude rat breast cancer brain metastasis model
Abstract
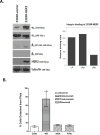
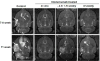
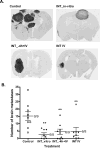
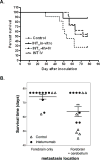
Brain metastases commonly occur in patients with breast, lung and melanoma systemic cancers. The anti-α(V) integrin monoclonal antibody intetumumab binds cell surface proteins important for adhesion, invasion and angiogenesis in the metastatic cascade. The objective of this study was to investigate the anti-metastatic effect of intetumumab in a hematogenous breast cancer brain metastasis model. Female nude rats received intra-carotid infusion of human brain-seeking metastatic breast cancer cells (231BR-HER2) and were randomly assigned into four groups: (1) control; (2) intetumumab mixed with cells in vitro 5 min before infusion without further treatment; (3) intetumumab intravenously 4 h before and weekly after cell infusion; (4) intetumumab intravenously weekly starting 7 days after cell infusion. Brain metastases were detected by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and immunohistochemistry. Comparisons were made using the Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunnett's test. Survival times were estimated using Kaplan-Meier analysis. All control rats with brain tissue available for histology (9 of 11 rats) developed multiple brain metastases (median = 14). Intetumumab treatment either in vitro prior to cell infusion or intravenous before or after cell infusion prevented metastasis formation on MRI and decreased the number of metastases on histology (median = 2, p = 0.0055), including 30 % of animals without detectable tumors at the end of the study. The overall survival was improved by intetumumab compared to controls (median 77+ vs. 52 days, p = 0.0277). Our results suggest that breast cancer patients at risk of metastases might benefit from early intetumumab treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
High αv Integrin Level of Cancer Cells Is Associated with Development of Brain Metastasis in Athymic Rats.Anticancer Res. 2017 Aug;37(8):4029-4040. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11788. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28739685 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-alphav integrin monoclonal antibody intetumumab enhances the efficacy of radiation therapy and reduces metastasis of human cancer xenografts in nude rats.Cancer Res. 2010 Oct 1;70(19):7591-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1639. Epub 2010 Sep 14. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20841470
-
Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging assessment of vascular targeting agent effects in rat intracerebral tumor models.Neuro Oncol. 2011 Jan;13(1):51-60. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noq150. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Neuro Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21123368 Free PMC article.
-
[Trastuzumab emtansine in the systemic treatment of HER-2-positive breast cancer brain metastases].Bull Cancer. 2016 May;103(5):507-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2016.02.005. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Bull Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26992855 Review. French. No abstract available.
-
Chemotherapy in breast cancer patients with brain metastases: have new chemotherapic agents changed the clinical outcome?Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2008 Dec;68(3):212-21. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2008.04.004. Epub 2008 Jun 12. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2008. PMID: 18550383 Review.
Cited by
-
Procyanidin B2 3,3″-di-O-gallate inhibits endothelial cells growth and motility by targeting VEGFR2 and integrin signaling pathways.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015;15(1):14-26. doi: 10.2174/1568009614666141229102254. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25552257 Free PMC article.
-
Formation, contents, functions of exosomes and their potential in lung cancer diagnostics and therapeutics.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Dec;12(23):3088-3100. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14217. Epub 2021 Nov 4. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34734680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breaking and entering into the CNS: clues from solid tumor and nonmalignant models with relevance to hematopoietic malignancies.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2014 Feb;31(2):257-67. doi: 10.1007/s10585-013-9623-4. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2014. PMID: 24306183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of the essential role of platelet-tumor cell interactions in metastasis progression using an agent-based model.Theor Biol Med Model. 2014 Apr 12;11:17. doi: 10.1186/1742-4682-11-17. Theor Biol Med Model. 2014. PMID: 24725600 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variants associated with colorectal brain metastases susceptibility and survival.Pharmacogenomics J. 2017 Jan;17(1):29-35. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2015.86. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Pharmacogenomics J. 2017. PMID: 26689941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palmieri D, Smith QR, Lockman PR, Bronder J, Gril B, Chambers AF, Weil RJ, Steeg PS. Brain metastases of breast cancer. Breast Dis. 2006;26:139–147. - PubMed
-
- Palmieri D, Bronder JL, Herring JM, Yoneda T, Weil RJ, Stark AM, Kurek R, Vega-Valle E, Feigenbaum L, Halverson D, Vortmeyer AO, Steinberg SM, Aldape K, Steeg PS. Her-2 overexpression increases the metastatic outgrowth of breast cancer cells in the brain. Cancer Res. 2007;67:4190–4198. - PubMed
-
- Santarelli JG, Sarkissian V, Hou LC, Veeravagu A, Tse V. Molecular events of brain metastasis. Neurosurg Focus. 2007;22:E1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

