Specific gene responses of Rhodococcus jostii RHA1 during growth in soil
- PMID: 22843521
- PMCID: PMC3457496
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00164-12
Specific gene responses of Rhodococcus jostii RHA1 during growth in soil
Abstract
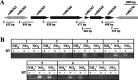
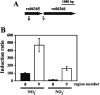
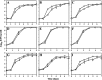
Transcriptome analysis of Rhodococcus jostii RHA1 during growth in sterilized soil was performed. A total of 165 soil-specific genes were identified by subtracting genes upregulated in late growth phases and on solid medium from 264 genes commonly upregulated during growth on biphenyl or pyruvate in sterilized soil. Classification of the 165 genes into functional categories indicated that this soil-specific group is rich in genes for the metabolism of fatty acids, amino acids, carbohydrates, and nitrogen and relatively poor in those for cellular processes and signaling. The ro06365-ro06369 gene cluster, in which ro06365 to ro06368 were highly upregulated in transcriptome analysis, was characterized further. ro06365 and ro06366 show similarity to a nitrite/nitrate transporter and a nitrite reductase, respectively, suggesting their involvement in nitrogen metabolism. A strain with an ro06366 deletion, D6366, showed growth retardation when we used nitrate as the sole nitrogen source and no growth when we used nitrite. A strain with a deletion of ro06365 to ro06368, DNop, utilized neither nitrite nor nitrate and recovered growth using nitrite and nitrate by introduction of the deleted genes. Both of the mutants showed growth retardation in sterilized soil, and the growth retardation of DNop was more significant than that of D6366. When these mutants were cultivated in medium containing the same proportions of ammonium, nitrate, and nitrite ions as those in the sterilized soil, they showed growth retardation similar to that in the soil. These results suggest that the ro06365-ro06369 gene cluster has a significant role in nitrogen utilization in sterilized soil.
Figures




References
-
- Adams MD, et al. 1990. Nucleotide sequence and genetic characterization reveal six essential genes for the LIV-I and LS transport systems of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 11436– 11443 - PubMed
-
- Araki N, et al. 2011. Glucose-mediated transcriptional repression of PCB/biphenyl catabolic genes in Rhodococcus jostii RHA1. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 20: 53– 62 - PubMed
-
- Ausubel FM, et al. 1990. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York, NY:
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

