MicroRNA-148b enhances the radiosensitivity of non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma cells by promoting radiation-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 22843616
- PMCID: PMC3393342
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrs002
MicroRNA-148b enhances the radiosensitivity of non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma cells by promoting radiation-induced apoptosis
Abstract
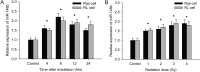
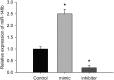
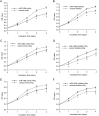
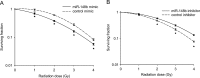
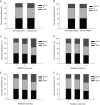
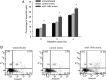
Growing evidence has demonstrated that microRNAs (miRNAs) play an important role in regulating cellular radiosensitivity. This study aimed to explore the role of miRNAs in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) radiosensitivity. Microarray was employed to compare the miRNA expression profiles in B cell lymphoma cell line Raji before and after a 2-Gy dose of radiation. A total of 20 differentially expressed miRNAs were identified including 10 up-regulated and 10 down-regulated (defined as P < 0.05). Among the differentially expressed miRNAs, miR-148b was up-regulated 1.53-fold in response to radiation treatment. A quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay confirmed the up-regulation of miR-148b after radiation. Transient transfection experiments showed that miR-148b was up-regulated by miR-148b mimic and down-regulated by miR-148b inhibitor in the Raji cells. A proliferation assay showed that miR-148b could inhibit the proliferation of Raji cells before and after radiation. A clonogenic assay demonstrated that miR-148b sensitized Raji cells to radiotherapy. MiR-148b did not affect the cell cycle profile of post-radiation Raji cells compared with controls. An apoptosis assay showed that miR-148b enhanced apoptosis of Raji cells after irradiation. Taken together, these results demonstrate that miR-148b increased the radiosensitivity of NHL cells probably by promoting radiation-induced apoptosis, which suggests that miR-148b plays an important role in the response of NHL to ionizing radiation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-148b enhances the radiosensitivity of B-cell lymphoma cells by targeting Bcl-w to promote apoptosis.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Jan 23;16(6):935-946. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.40756. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32140063 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR inhibits cell growth of human lymphoma cells by upregulation of miR-148b.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Aug;120(8):12348-12359. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28500. Epub 2019 Mar 8. J Cell Biochem. 2019. Retraction in: J Cell Biochem. 2021 Nov;122 Suppl 1:S37. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29996. PMID: 30848513 Retracted.
-
Rituximab enhances radiation-triggered apoptosis in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma cells via caspase-dependent and - independent mechanisms.J Radiat Res. 2006 Jun;47(2):183-96. doi: 10.1269/jrr.47.183. J Radiat Res. 2006. PMID: 16819145
-
miRNA-148b and its role in various cancers.Epigenomics. 2021 Dec;13(24):1939-1960. doi: 10.2217/epi-2021-0155. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Epigenomics. 2021. PMID: 34852637 Review.
-
Emergence of miR-34a in radiation therapy.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017 Jan;109:69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2016.11.017. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28010900 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Restoration of BRG1 inhibits proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer by regulating tumor suppressor miR-148b.Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Dec 2;8:3603-12. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S95500. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 26664144 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs, DNA Damage Response, and Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 12;17(12):2087. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122087. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27973455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-449a enhances radiosensitivity in CL1-0 lung adenocarcinoma cells.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 17;8(4):e62383. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062383. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23614048 Free PMC article.
-
Role of miR-100 in the radioresistance of colorectal cancer cells.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Jan 15;5(2):545-59. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25973296 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of MicroRNA-195-5p on Biological Behaviors and Radiosensitivity of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells via Targeting HOXA10.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Dec 7;2021:4522210. doi: 10.1155/2021/4522210. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34925694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fisher SG, Fisher RI. The epidemiology of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Oncogene. 2004;23(38):6524–34. - PubMed
-
- Miller TP, Dahlberg S, Cassady JR, et al. Chemotherapy alone compared with chemotherapy plus radiotherapy for localized intermediate- and high-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(1):21–6. - PubMed
-
- Ferreri AJ, Dell'Oro S, Reni M, et al. Consolidation radiotherapy to bulky or semibulky lesions in the management of stage III-IV diffuse large B cell lymphomas. Oncology. 2000;58(3):219–26. - PubMed

