Synergistic effect of heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin and X-rays, but not carbon-ion beams, on lethality in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
- PMID: 22843619
- PMCID: PMC3393353
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrs012
Synergistic effect of heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin and X-rays, but not carbon-ion beams, on lethality in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
Abstract
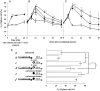
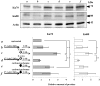
The purpose of this study is to clarify the effect of a heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG), in combination with X-rays or carbon-ion beams on cell killing in human oral squamous cell carcinoma LMF4 cells. Cell survival was measured by colony formation assay. Cell-cycle distribution was analyzed by flow cytometry. Expression of DNA repair-related proteins was investigated by western blotting. The results showed 17-AAG to have synergistic effects on cell lethality with X-rays, but not with carbon-ion beams. The 17-AAG decreased G(2)/M arrest induced by X-rays, but not by carbon-ion beams. Both X-ray and carbon-ion irradiation up-regulated expression of non-homologous end-joining-associated proteins, Ku70 and Ku80, but 17-AAG inhibited only X-ray-induced up-regulation of these proteins. These results show that 17-AAG with X-rays releases G(2)/M phase arrest; cells carrying misrepaired DNA damage then move on to the G(1) phase. We demonstrate, for the first time, that the radiosensitization effect of 17-AAG is not seen with carbon-ion beams because 17-AAG does not affect these changes.
Figures

References
-
- Takahashi A, Ohnishi K, Wang X. The dependence of p53 on the radiation enhancement of thermosensitivity at different LET. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;47:489–94. - PubMed
-
- Iwadate Y, Mizoe J, Osaka Y, et al. High linear energy transfer carbon radiation effectively kills cultured glioma cells with either mutant or wild-type p53. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;50:803–8. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi A, Matsumoto H, Yuki K, et al. High-LET radiation enhanced apoptosis but not necrosis regardless of p53 status. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;60:591–7. - PubMed
-
- Ogata T, Teshima T, Inaoka M, et al. Carbon ion irradiation suppresses metastatic potential of human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells through the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. J Radiat Res. 2011;52:374–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

