Biophysical characterization of a relativistic proton beam for image-guided radiosurgery
- PMID: 22843629
- PMCID: PMC3393345
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrs007
Biophysical characterization of a relativistic proton beam for image-guided radiosurgery
Abstract
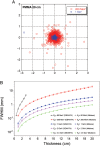
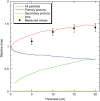
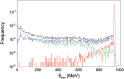
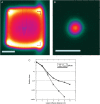
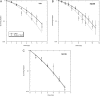
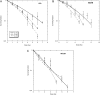
We measured the physical and radiobiological characteristics of 1 GeV protons for possible applications in stereotactic radiosurgery (image-guided plateau-proton radiosurgery). A proton beam was accelerated at 1 GeV at the Brookhaven National Laboratory (Upton, NY) and a target in polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) was used. Clonogenic survival was measured after exposures to 1-10 Gy in three mammalian cell lines. Measurements and simulations demonstrate that the lateral scattering of the beam is very small. The lateral dose profile was measured with or without the 20-cm plastic target, showing no significant differences up to 2 cm from the axis A large number of secondary swift protons are produced in the target and this leads to an increase of approximately 40% in the measured dose on the beam axis at 20 cm depth. The relative biological effectiveness at 10% survival level ranged between 1.0 and 1.2 on the beam axis, and was slightly higher off-axis. The very low lateral scattering of relativistic protons and the possibility of using online proton radiography during the treatment make them attractive for image-guided plateau (non-Bragg peak) stereotactic radiosurgery.
Figures
References
-
- Halperin EC. Particle therapy and treatment of cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:676–85. - PubMed
-
- Bert C, Engenhart-Cabillic R, Durante M. Particle therapy for noncancer diseases. Med Phys. 2012;39:1716–27. - PubMed
-
- Durante M, Loeffler JS. Charged particles in radiation oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010;7:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Pedroni E, Scheib S, Böhringer T, et al. Experimental characterization and physical modelling of the dose distribution of scanned proton pencil beams. Phys Med Biol. 2005;50:541–61. - PubMed

