C-reactive protein/interleukin-6 ratio as marker of the size of the uncomplicated thoracic aortic aneurysms
- PMID: 22843654
- PMCID: PMC3480603
- DOI: 10.1093/icvts/ivs331
C-reactive protein/interleukin-6 ratio as marker of the size of the uncomplicated thoracic aortic aneurysms
Abstract
Objectives: The role of C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) as markers in the prognosis of asymptomatic thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) patients has not been well established. As such, we evaluated a group of patients for a possible association between serum CRP and IL-6 and aneurysm dimension.
Methods: Serum CRP and IL-6 were determined and aneurysmal size was measured in 26 patients with TAA.
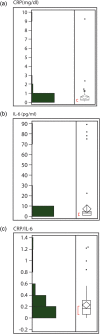
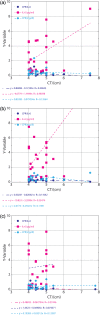
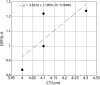
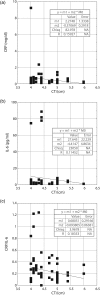
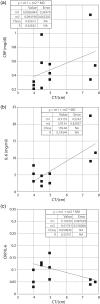
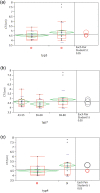
Results: The mean (SD) CRP and IL-6 were 0.58 (1.07) and 7.47 (17.78) pg/ml, respectively. Serum CRP, IL-6 and the ratio CRP/IL-6 correlated with the descending aortic aneurysmal dimension (r = 0.426, r = 0.743 and r = 0.328, respectively). A significant correlation was also found between values of the ratio above 0.8 and aneurysmal dimension (both ascending and descending aneurysms) (r = 0.785). Additionally, a significant association between smoking, age group above 69 years and dyslipidemia and aneurysm dimension was established (P = 0.002, P = 0.061 and P = 0.070, respectively).
Conclusions: This report shows that serum CRP, IL-6 levels and the ratio CRP/IL-6 are associated with descending aortic aneurysmal dimensions. Also values of the ratio CRP/IL-6 above 0.8 are associated with aneurysmal dimensions for both ascending and descending aortic aneurysms. It is still early to establish the clinical significance of those findings, and further studies with larger groups of patients with longer follow-up are required in order to truly assess the usefulness of the serum CRP and IL-6 as markers in relation to the progression of the disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aortic aneurysms secrete interleukin-6 into the circulation.J Vasc Surg. 2007 Feb;45(2):350-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2006.09.049. J Vasc Surg. 2007. PMID: 17264016
-
Clinical significance of preoperative serum vascular endothelial growth factor, interleukin-6, and C-reactive protein level in colorectal cancer.BMC Cancer. 2010 May 14;10:203. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-203. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20465852 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory response and renal function following endovascular repair of the descending thoracic aorta.J Endovasc Ther. 2015 Apr;22(2):201-6. doi: 10.1177/1526602815573227. J Endovasc Ther. 2015. PMID: 25809362
-
Serum C-reactive protein level is associated with abdominal aortic aneurysm size and may be produced by aneurysmal tissue.Circulation. 2003 Mar 4;107(8):1103-5. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000059938.95404.92. Circulation. 2003. PMID: 12615785
-
What Is the Normal Trajectory of Interleukin-6 and C-reactive Protein in the Hours and Days Immediately After TKA?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019 Jan;477(1):41-46. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000332. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019. PMID: 30794227 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association Between Red Blood Cell Distribution Width-to-Albumin Ratio and Prognosis of Patients with Aortic Aneurysms.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Oct 1;14:6287-6294. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S328035. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34621131 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress parameters in patients with ascending aortic dilatation.Turk J Med Sci. 2020 Aug 26;50(5):1323-1329. doi: 10.3906/sag-1909-183. Turk J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32421280 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 Receptor Inhibition Prevents Descending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Formation.Ann Thorac Surg. 2015 Nov;100(5):1620-6. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2015.05.009. Epub 2015 Jul 10. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015. PMID: 26165482 Free PMC article.
-
New systemic inflammatory indices as predictors of ascending aortic dilation in children with bicuspid aortic valve: A retrospective cross-sectional study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 6;103(49):e40904. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040904. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39654160 Free PMC article.
-
A porcine model of thoracic aortic aneurysms created with a retrievable drug infusion stent graft mirrors human aneurysm pathophysiology.JVS Vasc Sci. 2024 Jul 2;5:100212. doi: 10.1016/j.jvssci.2024.100212. eCollection 2024. JVS Vasc Sci. 2024. PMID: 39188992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reynolds GD, Vance RP. C-Reactive protein immunohistochemical localization in normal and atherosclerotic human aortas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1987;111:265–9. - PubMed
-
- Smallwood L, Allcock R, van Bockxmeer F, Warrington N, Palmer LJ, Iacopetta B, et al. Polymorphisms of the interleucin-6 gene promoter and abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2008;35:31–6. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy RP, Hennekens CH. Inflammation, aspirin and the risk of cardiovascular disease in apparently healthy men. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:973–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

