zCall: a rare variant caller for array-based genotyping: genetics and population analysis
- PMID: 22843986
- PMCID: PMC3463112
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts479
zCall: a rare variant caller for array-based genotyping: genetics and population analysis
Abstract
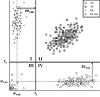
Summary: zCall is a variant caller specifically designed for calling rare single-nucleotide polymorphisms from array-based technology. This caller is implemented as a post-processing step after a default calling algorithm has been applied. The algorithm uses the intensity profile of the common allele homozygote cluster to define the location of the other two genotype clusters. We demonstrate improved detection of rare alleles when applying zCall to samples that have both Illumina Infinium HumanExome BeadChip and exome sequencing data available.
Availability: http://atguweb.mgh.harvard.edu/apps/zcall.
Contact: bneale@broadinstitute.org
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures
References
-
- Botstein D, Risch N. Discovering genotypes underlying human phenotypes: past successes for mendelian disease, future approaches for complex disease. Nat. Genet. 2003;33:228–237. - PubMed
-
- Illumina Inc. Illumina GenCall Data Analysis Software. TECHNOLOGY SPOTLIGHT. 2005 Available at http://www.illumina.com/Documents/products/technotes/technote_gencall_da... (8 August 2012)
-
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

