Comparison of visual grading and free-response ROC analyses for assessment of image-processing algorithms in digital mammography
- PMID: 22844032
- PMCID: PMC3611729
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr/22608279
Comparison of visual grading and free-response ROC analyses for assessment of image-processing algorithms in digital mammography
Abstract
Objective: To compare two methods for assessment of image-processing algorithms in digital mammography: free-response receiver operating characteristic (FROC) for the specific task of microcalcification detection and visual grading analysis (VGA).
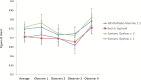
Methods: The FROC study was conducted prior to the VGA study reported here. 200 raw data files of low breast density (Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System I-II) mammograms (Novation DR, Siemens, Germany)-100 of which abnormal-were processed by four image-processing algorithms: Raffaello (IMS, Bologna, Italy), Sigmoid (Sectra, Linköping, Sweden), and OpView v. 2 and v. 1 (Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). Four radiologists assessed the mammograms for the detection of microcalcifications. 8 months after the FROC study, a subset (200) of the 800 images was reinterpreted by the same radiologists, using the VGA methodology in a side-by-side approach. The VGA grading was based on noise, saturation, contrast, sharpness and confidence with the image in terms of normal structures. Ordinal logistic regression was applied; OpView v. 1 was the reference processing algorithm.
Results: In the FROC study all algorithms performed better than OpView v. 1. From the current VGA study and for confidence with the image, Sigmoid and Raffaello were significantly worse (p<0.001) than OpView v. 1; OpView v. 2 was significantly better (p=0.01). For the image quality criteria, results were mixed; Raffaello and Sigmoid for example were better than OpView v. 1 for sharpness and contrast (although not always significantly).
Conclusion: VGA and FROC discordant results should be attributed to the different clinical task addressed.
Advances in knowledge: The method to use for image-processing assessment depends on the clinical task tested.
Figures


References
-
- Cole EB, Pisano ED, Kistner EO, Muller KE, Brown ME, Feig SA, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of digital mammography in patients with dense breasts who underwent problem-solving mammography: effects of image processing and lesion type. Radiology 2003;226:153–60 - PubMed
-
- Cole EB, Pisano ED, Zeng D, Muller K, Aylward SR, Park S, et al. The effects of gray scale image processing on digital mammography interpretation performance. Acad Radiol 2005;12:585–95 - PubMed
-
- Pisano ED, Cole EB, Hemminger BM, Yaffe MJ, Aylward SR, Maidment AD, et al. Image processing algorithms for digital mammography: a pictorial essay. Radiographics 2000;20:1479–91 - PubMed
-
- Pisano ED, Gatsonis CA, Yaffe MJ, Hendrick RE, Tosteson AN, Fryback DG, et al. American College of Radiology Imaging Network digital mammographic imaging screening trial: objectives and methodology. Radiology 2005;236:404–12 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

