Rapid turnover of long noncoding RNAs and the evolution of gene expression
- PMID: 22844254
- PMCID: PMC3406015
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002841
Rapid turnover of long noncoding RNAs and the evolution of gene expression
Abstract
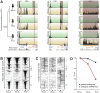
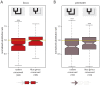
A large proportion of functional sequence within mammalian genomes falls outside protein-coding exons and can be transcribed into long RNAs. However, the roles in mammalian biology of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) are not well understood. Few lncRNAs have experimentally determined roles, with some of these being lineage-specific. Determining the extent by which transcription of lncRNA loci is retained or lost across multiple evolutionary lineages is essential if we are to understand their contribution to mammalian biology and to lineage-specific traits. Here, we experimentally investigated the conservation of lncRNA expression among closely related rodent species, allowing the evolution of DNA sequence to be uncoupled from evolution of transcript expression. We generated total RNA (RNAseq) and H3K4me3-bound (ChIPseq) DNA data, and combined both to construct catalogues of transcripts expressed in the adult liver of Mus musculus domesticus (C57BL/6J), Mus musculus castaneus, and Rattus norvegicus. We estimated the rate of transcriptional turnover of lncRNAs and investigated the effects of their lineage-specific birth or death. LncRNA transcription showed considerably greater gain and loss during rodent evolution, compared with protein-coding genes. Nucleotide substitution rates were found to mirror the in vivo transcriptional conservation of intergenic lncRNAs between rodents: only the sequences of noncoding loci with conserved transcription were constrained. Finally, we found that lineage-specific intergenic lncRNAs appear to be associated with modestly elevated expression of genomically neighbouring protein-coding genes. Our findings show that nearly half of intergenic lncRNA loci have been gained or lost since the last common ancestor of mouse and rat, and they predict that such rapid transcriptional turnover contributes to the evolution of tissue- and lineage-specific gene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Bertone P, Stolc V, Royce TE, Rozowsky JS, Urban AE, et al. Global identification of human transcribed sequences with genome tiling arrays. Science. 2004;306:2242–2246. - PubMed
-
- Carninci P, Kasukawa T, Katayama S, Gough J, Frith MC, et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science. 2005;309:1559–1563. - PubMed
-
- Cloonan N, Forrest AR, Kolle G, Gardiner BB, Faulkner GJ, et al. Stem cell transcriptome profiling via massive-scale mRNA sequencing. Nat Methods. 2008;5:613–619. - PubMed
-
- Okazaki Y, Furuno M, Kasukawa T, Adachi J, Bono H, et al. Analysis of the mouse transcriptome based on functional annotation of 60,770 full-length cDNAs. Nature. 2002;420:563–573. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

