Expression of K19 and K7 in dysplastic nodules and hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 22844356
- PMCID: PMC3402733
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2012.731
Expression of K19 and K7 in dysplastic nodules and hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
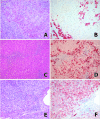
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common types of malignant tumors characterized by a multistep process of tumor development. Nodular lesions that differ from the surrounding liver parenchyma and are characterized by cytological or structural atypia are termed dysplastic nodules (DNs). DNs are well-known precancerous HCC lesions. Expression of keratin (K) 19 and K7, molecular markers of hepatic progenitor cells and cholangiocytes, has been reported in certain HCCs. However, it remains unclear whether K19-positive HCC cells are derived from true hepatic progenitor cells or mature cells that have undergone a dedifferentiation or a transdifferentiation process. In total, 107 tissue sections (13 low-grade DNs, 15 high-grade DNs, 27 small HCCs and 52 large HCCs) from resected liver samples and 132 HCC tissue microarray (TMA) cores were subjected to immunohistochemical analysis for K19 and K7. Clinicopathological data of the HCC patients were evaluated. K19 expression was found in 0% of DNs, 19% of small HCCs (≤2 cm), 8% of large HCCs (>2 cm) and 8% of TMA samples. K7 expression was found in 14% of DNs, 41% of small HCCs, 15% of large HCCs and 6% of TMA samples. Among the five K19-positive small HCCs, four were distinctly nodular and one tumor was an infiltrative type. No vaguely nodular HCC was positive for K19. K19 expression was significantly associated with histological grade (P=0.023), serum α-fetoprotein level (P=0.001) and K7 expression (P=0.001) in HCC. K19 expression was an independent prognostic factor for overall survival in non-viral HCC patients (P=0.003). K19 expression is extremely rare in DNs and occurs in progressed small HCCs. Our results suggest that K19 expression may be an acquired feature of carcinoma cells during HCC progression in certain HCCs.
Figures

References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Park YN. Update on precursor and early lesions of hepatocellular carcinomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:704–715. - PubMed
-
- Theise ND, Curado MP, Franceschi S, Hytiroglou P, Kudo M, Park YN, Sakamoto M, Torbenson M, Wee A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. In: Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND, editors. WHO Classification Of Tumours Of The Digestive System. 4th edition. IARC Press; Lyon: 2010. pp. 205–216.
-
- Durnez A, Verslype C, Nevens F, Fevery J, Aerts R, Pirenne J, Lesaffre E, Libbrecht L, Desmet V, Roskams T. The clinicopathological and prognostic relevance of cytokeratin 7 and 19 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. A possible progenitor cell origin. Histopathology. 2006;49:138–151. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
