Biomarkers of inflammation, immunosuppression and stress with active disease are revealed by metabolomic profiling of tuberculosis patients
- PMID: 22844400
- PMCID: PMC3402490
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040221
Biomarkers of inflammation, immunosuppression and stress with active disease are revealed by metabolomic profiling of tuberculosis patients
Erratum in
-
Correction: Biomarkers of Inflammation, Immunosuppression and Stress Are Revealed by Metabolomic Profiling of Tuberculosis Patients.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 31;11(3):e0153050. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153050. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27031112 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
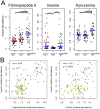
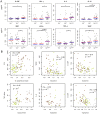
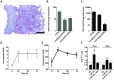
Although tuberculosis (TB) causes more deaths than any other pathogen, most infected individuals harbor the pathogen without signs of disease. We explored the metabolome of >400 small molecules in serum of uninfected individuals, latently infected healthy individuals and patients with active TB. We identified changes in amino acid, lipid and nucleotide metabolism pathways, providing evidence for anti-inflammatory metabolomic changes in TB. Metabolic profiles indicate increased activity of indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase 1 (IDO1), decreased phospholipase activity, increased abundance of adenosine metabolism products, as well as indicators of fibrotic lesions in active disease as compared to latent infection. Consistent with our predictions, we experimentally demonstrate TB-induced IDO1 activity. Furthermore, we demonstrate a link between metabolic profiles and cytokine signaling. Finally, we show that 20 metabolites are sufficient for robust discrimination of TB patients from healthy individuals. Our results provide specific insights into the biology of TB and pave the way for the rational development of metabolic biomarkers for TB.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Kaddurah-Daouk R, Kristal BS, Weinshilboum RM. Metabolomics: a global biochemical approach to drug response and disease. Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008;48:653–683. - PubMed
-
- Han X, Holtzman M, McKeel DW, Jr, Kelley J, Morris JC. Substantial sulfatide deficiency and ceramide elevation in very early Alzheimer’s disease: potential role in disease pathogenesis. J Neurochem 82: 809–818. 0997 [pii] 2002. - PubMed
-
- Bogdanov M, Matson WR, Wang L, Matson T, Saunders-Pullman R, et al. Metabolomic profiling to develop blood biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2008;131:389–396. - PubMed
-
- Sabatine MS, Liu E, Morrow DA, Heller E, McCarroll R, et al. Metabolomic identification of novel biomarkers of myocardial ischemia. Circulation. 2005;112:3868–3875. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

