Clonal analysis in recurrent astrocytic, oligoastrocytic and oligodendroglial tumors implicates IDH1- mutation as common tumor initiating event
- PMID: 22844452
- PMCID: PMC3402513
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041298
Clonal analysis in recurrent astrocytic, oligoastrocytic and oligodendroglial tumors implicates IDH1- mutation as common tumor initiating event
Abstract
Background: To investigate the dynamics of inter- and intratumoral molecular alterations during tumor progression in recurrent gliomas.
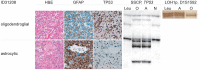
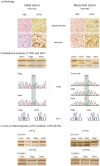
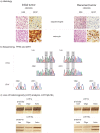
Methodology/principal findings: To address intertumoral heterogeneity we investigated non-microdissected tumor tissue of 106 gliomas representing 51 recurrent tumors. To address intratumoral heterogeneity a set of 16 gliomas representing 7 tumor pairs with at least one recurrence, and 4 single mixed gliomas were investigated by microdissection of distinct oligodendroglial and astrocytic tumor components. All tumors and tumor components were analyzed for allelic loss of 1p/19q (LOH 1p/19q), for TP53- mutations and for R132 mutations in the IDH1 gene. The investigation of non-microdissected tumor tissue revealed clonality in 75% (38/51). Aberrant molecular alterations upon recurrence were detected in 25% (13/51). 64% (9/14) of these were novel and associated with tumor progression. Loss of previously detected alterations was observed in 36% (5/14). One tumor pair (1/14; 7%) was significant for both. Intratumoral clonality was detected in 57% (4/7) of the microdissected tumor pairs and in 75% (3/4) of single microdissected tumors. 43% (3/7) of tumor pairs and one single tumor (25%) revealed intratumoral heterogeneity. While intratumoral heterogeneity affected both the TP53- mutational status and the LOH1p/19q status, all tumors with intratumoral heterogeneity shared the R132 IDH1- mutation as a common feature in both their microdissected components.
Conclusions/significance: The majority of recurrent gliomas are of monoclonal origin. However, the detection of divertive tumor cell clones in morphological distinct tumor components sharing IDH1- mutations as early event may provide insight into the tumorigenesis of true mixed gliomas.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Cairncross JG, Ueki K, Zlatescu MC, Lisle DK, Finkelstein DM, et al. Specific genetic predictors of chemotherapeutic response and survival in patients with anaplastic oligodendrogliomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90:1473–1479. - PubMed
-
- Smith JS, Perry A, Borell TJ, Lee HK, O'Fallon J, et al. Alterations of chromosome arms 1p and 19q as predictors of survival in oligodendrogliomas, astrocytomas, and mixed oligoastrocytomas. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:636–645. - PubMed
-
- Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, Hamou MF, de Tribolet N, et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:997–1003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

