β-Glucan derived from Aureobasidium pullulans is effective for the prevention of influenza in mice
- PMID: 22844473
- PMCID: PMC3402398
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041399
β-Glucan derived from Aureobasidium pullulans is effective for the prevention of influenza in mice
Abstract
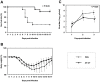
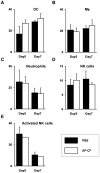
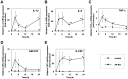
β-(1→3)-D-glucans with β-(1→6)-glycosidic linked branches produced by mushrooms, yeast and fungi are known to be an immune activation agent, and are used in anti-cancer drugs or health-promoting foods. In this report, we demonstrate that oral administration of Aureobasidium pullulans-cultured fluid (AP-CF) enriched with the β-(1→3),(1→6)-D-glucan exhibits efficacy to protect mice infected with a lethal titer of the A/Puerto Rico/8/34 (PR8; H1N1) strain of influenza virus. The survival rate of the mice significantly increased by AP-CF administration after sublethal infection of PR8 virus. The virus titer in the mouse lung homogenates was significantly decreased by AP-CF administration. No significant difference in the mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines, and in the population of lymphocytes was observed in the lungs of mice administered with AP-CF. Interestingly, expression level for the mRNA of virus sensors, RIG-I (retinoic acid-inducible gene-I) and MDA5 (melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5) strongly increased at 5 hours after the stimulation of A. pullulans-produced purified β-(1→3),(1→6)-D-glucan (AP-BG) in murine macrophage-derived RAW264.7 cells. Furthermore, the replication of PR8 virus was significantly repressed by pre-treatment of AP-BG. These findings suggest the increased expression of virus sensors is effective for the prevention of influenza by the inhibition of viral replication with the administration of AP-CF.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Akramiene D, Kondrotas A, Didziapetriene J, Kevelaitis E. Effects of beta-glucans on the immune system. Medicina (Kaunas) 2007;43:597–606. - PubMed
-
- Novak M, Vetvicka V. Glucans as biological response modifiers. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2009;9:67–75. - PubMed
-
- Chaung HC, Huang TC, Yu JH, Wu ML, Chung WB. Immunomodulatory effects of beta-glucans on porcine alveolar macrophages and bone marrow haematopoietic cell-derived dendritic cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2009;131:147–157. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Gunn L, Hansen R, Yan J. Yeast-derived beta-glucan in combination with anti-tumor monoclonal antibody therapy in cancer. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2009;4:101–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

