Micro-RNA-195 and -451 regulate the LKB1/AMPK signaling axis by targeting MO25
- PMID: 22844503
- PMCID: PMC3402395
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041574
Micro-RNA-195 and -451 regulate the LKB1/AMPK signaling axis by targeting MO25
Abstract
Background: Recently, MicroRNAs (miR) and AMP-kinase (AMPK) have emerged as prominent players in the development of cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. We hypothesized that components of the adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase (AMPK) pathway are targeted by miRs and alter AMPK signaling during pathological cardiac stress.
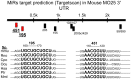
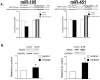
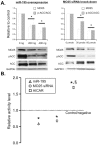
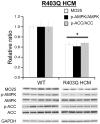
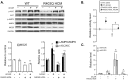
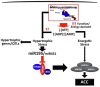
Methodology/principal findings: Using a mouse model of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), we demonstrated early elevation of miR-195 and miR-451 in HCM hearts, which targets MO25, a central component of the MO25/STRAD/LKB1 complex that acts as an upstream kinase for AMPK. We show functional targeting of MO25 by miR-195 and -451. Further in vitro interrogation of MO25 as a functional target validated this hypothesis where over-expression of miR-195 in C2C12 cells knocked down MO25 expression levels and downstream AMPK signaling (phosphorylation of Acetyl CoA carboxylase [ACC] and AMPK activity assay), similar to MO25 knockdown in C2C12 cells by siRNA. Parallel changes were measured in 60 day R403Q HCM male hearts that were rescued by short-term administration of AICAR, an AMPK agonist.
Conclusions/significance: Elevated miR-195 targets the LKB1/AMPK signaling axis in HCM progression and implicates a functional role in HCM disease progression. MiR-195 may serve as potential therapeutics or therapeutic targets for heart disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Complexes between the LKB1 tumor suppressor, STRAD alpha/beta and MO25 alpha/beta are upstream kinases in the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade.J Biol. 2003;2(4):28. doi: 10.1186/1475-4924-2-28. Epub 2003 Sep 24. J Biol. 2003. PMID: 14511394 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of 3-phosphoglycerate and other metabolites on the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase by LKB1-STRAD-MO25.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Feb;292(2):E400-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00322.2006. Epub 2006 Sep 19. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 16985256
-
Thyroid hormone effects on LKB1, MO25, phospho-AMPK, phospho-CREB, and PGC-1alpha in rat muscle.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008 Oct;105(4):1218-27. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00997.2007. Epub 2008 Jul 31. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008. PMID: 18669938
-
Opinion: alternative views of AMP-activated protein kinase.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2007;47(3):321-31. doi: 10.1007/s12013-007-0005-x. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2007. PMID: 17652778 Review.
-
Targeting AMPK for cardiac protection: opportunities and challenges.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011 Oct;51(4):548-53. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.12.004. Epub 2010 Dec 13. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21147121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LKB1 signaling is altered in skeletal muscle of a Duchenne muscular dystrophy mouse model.Dis Model Mech. 2023 Jul 1;16(7):dmm049930. doi: 10.1242/dmm.049930. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Dis Model Mech. 2023. PMID: 37427454 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-195 controls MICU1 expression and tumor growth in ovarian cancer.EMBO Rep. 2020 Oct 5;21(10):e48483. doi: 10.15252/embr.201948483. Epub 2020 Aug 27. EMBO Rep. 2020. PMID: 32851774 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Doxorubicin-Induced Vascular Remodeling.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 12;25(24):13335. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413335. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Receptor Interacting Protein Kinases Attenuates Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy Induced by Palmitic Acid.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:1451676. doi: 10.1155/2016/1451676. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 27057269 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Enhances Autophagy via the Consumption of miR-326 in a Mouse Model of Acute Lung Injury.Biochem Genet. 2025 Jan 27. doi: 10.1007/s10528-025-11040-3. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 39869241
References
-
- Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–269. - PubMed
-
- Glazov EA, Pheasant M, Nahkuri S, Mattick JS. Evidence for control of splicing by alternative RNA secondary structures in Dipteran homothorax pre-mRNA. RNA Biol. 2006;3:36–39. - PubMed
-
- Hammond SM. RNAi, microRNAs, and human disease. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006;58:s63–68. - PubMed
-
- Ikeda S, Kong SW, Lu J, Bisping E, Zhang H, et al. Altered microRNA expression in human heart disease. Physiol Genomics. 2007;31:367–373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

