MC-12, an annexin A1-based peptide, is effective in the treatment of experimental colitis
- PMID: 22844504
- PMCID: PMC3402399
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041585
MC-12, an annexin A1-based peptide, is effective in the treatment of experimental colitis
Abstract
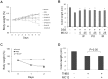
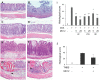
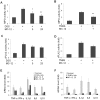
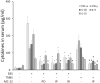
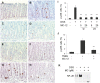
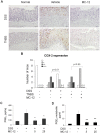
Annexin A1 (ANXA1) inhibits NF-κB, a key regulator of inflammation, the common pathophysiological mechanism of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). MC-12, an ANXA1-based tripeptide, suppresses NF-κB activation. Here, we determined the efficacy of MC-12 in the control of IBD. Mice with colitis induced by dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) or 2,4,6-trinitro benzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) were treated with various doses of MC-12 administered intraperitoneally, orally or intrarectally. We determined colon length and the histological score of colitis, and assayed: in colon tissue the levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10 by RT-PCR; prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)), cytoplasmic phospholipase A(2) (cPLA(2)) and myeloperoxidase by immunoassay; and COX-2 and NF- κB by immunohistochemistry; and in serum the levels of various cytokines by immunoassay. In both models MC-12: reversed dose-dependently colonic inflammation; inhibited by up to 47% myeloperoxidase activity; had a minimal effect on cytoplasmic phospholipase A(2); reduced significantly the induced levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10, returning them to baseline. DSS and TNBS markedly activated NF-κB in colonic epithelial cells and MC-12 decreased this effect by 85.8% and 72.5%, respectively. MC-12 had a similar effect in cultured NCM460 normal colon epithelial cells. Finally, MC-12 suppressed the induction of COX-2 expression, the level of PGE(2) in the colon and PGE(2) metabolite in serum. In conclusion, MC-12, representing a novel class of short peptide inhibitors of NF-κB, has a strong effect against colitis in two preclinical models recapitulating features of human IBD. Its mechanism of action is complex and includes pronounced inhibition of NF-κB. MC-12 merits further development as an agent for the control of IBD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitor of apoptosis-stimulating p53 protein protects against inflammatory bowel disease in mice models by inhibiting the nuclear factor kappa B signaling.Clin Exp Immunol. 2021 Aug;205(2):246-256. doi: 10.1111/cei.13613. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Clin Exp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33942299 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin improves TNBS-induced colitis in rats by inhibiting IL-27 expression via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Planta Med. 2013 Jan;79(2):102-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1328057. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Planta Med. 2013. PMID: 23250811
-
Oridonin derivative ameliorates experimental colitis by inhibiting activated T-cells and translocation of nuclear factor-kappa B.J Dig Dis. 2016 Feb;17(2):104-12. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12314. J Dig Dis. 2016. PMID: 26718746
-
Elucidation of colon-protective efficacy of diosgenin in experimental TNBS-induced colitis: inhibition of NF-κB/IkB-α and Bax/Caspase-1 signaling pathways.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2020 Sep;84(9):1903-1912. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2020.1776590. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32525764
-
Efficacy of extracellular vesicles as a cell-free therapy in colitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 26;14:1260134. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1260134. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37954844 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Influenza A virus enhances its propagation through the modulation of Annexin-A1 dependent endosomal trafficking and apoptosis.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Jul;23(7):1243-56. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.19. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 26943321 Free PMC article.
-
Peptides as Therapeutic Agents for Inflammatory-Related Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 11;19(9):2714. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092714. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30208640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An engineered cyclic peptide alleviates symptoms of inflammation in a murine model of inflammatory bowel disease.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 16;292(24):10288-10294. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.779215. Epub 2017 May 4. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28473469 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Profiles of GILZ and Annexin A1 in Human Oral Candidiasis and Lichen Planus.Cells. 2022 Apr 27;11(9):1470. doi: 10.3390/cells11091470. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563776 Free PMC article.
-
A murine colitis model developed using a combination of dextran sulfate sodium and Citrobacter rodentium.J Microbiol. 2018 Apr;56(4):272-279. doi: 10.1007/s12275-018-7504-x. Epub 2018 Apr 2. J Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29611140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vatn MH. Natural history and complications of IBD. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2009;11:481–487. - PubMed
-
- Mayer L. Evolving paradigms in the pathogenesis of IBD. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Szigethy E, McLafferty L, Goyal A. Inflammatory bowel disease. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am 19: 301–318, ix. 2010. - PubMed
-
- Devlin SM, Panaccione R. Evolving inflammatory bowel disease treatment paradigms: top-down versus step-up. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2009;38:577–594. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

