MicroRNA regulation of the synaptic plasticity-related gene Arc
- PMID: 22844515
- PMCID: PMC3406043
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041688
MicroRNA regulation of the synaptic plasticity-related gene Arc
Abstract
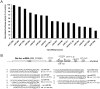
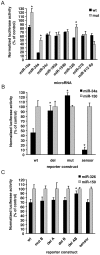
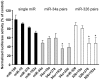
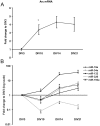
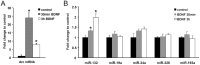
Expression of activity-regulated cytoskeleton associated protein (Arc) is crucial for diverse types of experience-dependent synaptic plasticity and long-term memory in mammals. However, the mechanisms governing Arc-specific translation are little understood. Here, we asked whether Arc translation is regulated by microRNAs. Bioinformatic analysis predicted numerous candidate miRNA binding sites within the Arc 3'-untranslated region (UTR). Transfection of the corresponding microRNAs in human embryonic kidney cells inhibited expression of an Arc 3'UTR luciferase reporter from between 10 to 70% across 16 microRNAs tested. Point mutation and deletion of the microRNA-binding seed-region for miR-34a, miR-326, and miR-19a partially or fully rescued reporter expression. In addition, expression of specific microRNA pairs synergistically modulated Arc reporter expression. In primary rat hippocampal neuronal cultures, ectopic expression of miR-34a, miR-193a, or miR-326, downregulated endogenous Arc protein expression in response to BDNF treatment. Conversely, treatment of neurons with cell-penetrating, peptide nucleic acid (PNA) inhibitors of miR-326 enhanced Arc mRNA expression. BDNF dramatically upregulated neuronal expression of Arc mRNA and miR-132, a known BDNF-induced miRNA, without affecting expression of Arc-targeting miRNAs. Developmentally, miR-132 was upregulated at day 10 in vitro whereas Arc-targeting miRNAs were downregulated. In the adult brain, LTP induction in the dentate gyrus triggered massive upregulation of Arc and upregulation of miR-132 without affecting levels of mature Arc-targeting miRNAs. Turning to examine miRNA localization, qPCR analysis of dentate gyrus synaptoneurosome and total lysates fractions demonstrated synaptic enrichment relative to small nucleolar RNA. In conclusion, we find that Arc is regulated by multiple miRNAs and modulated by specific miRNA pairs in vitro. Furthermore, we show that, in contrast to miR-132, steady state levels of Arc-targeting miRNAs do not change in response to activity-dependent expression of Arc in hippocampal neurons in vitro or during LTP in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
An activity-regulated microRNA, miR-188, controls dendritic plasticity and synaptic transmission by downregulating neuropilin-2.J Neurosci. 2012 Apr 18;32(16):5678-5687. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6471-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22514329 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces long-term potentiation in intact adult hippocampus: requirement for ERK activation coupled to CREB and upregulation of Arc synthesis.J Neurosci. 2002 Mar 1;22(5):1532-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-05-01532.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11880483 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic identification of 3'-UTR regulatory elements in activity-dependent mRNA stability in hippocampal neurons.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Sep 26;369(1652):20130509. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0509. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25135970 Free PMC article.
-
The immediate early gene arc/arg3.1: regulation, mechanisms, and function.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 12;28(46):11760-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3864-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19005037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF mechanisms in late LTP formation: A synthesis and breakdown.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:664-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.06.024. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23831365 Review.
Cited by
-
microRNA miR-34a regulates cytodifferentiation and targets multi-signaling pathways in human dental papilla cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50090. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050090. Epub 2012 Nov 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23226240 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of long-term potentiation.Neurogenetics. 2016 Oct;17(4):201-210. doi: 10.1007/s10048-016-0489-x. Epub 2016 Jun 18. Neurogenetics. 2016. PMID: 27318935 Review.
-
MicroRNA-132 is overexpressed in fetuses with late-onset fetal growth restriction.Health Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 15;5(2):e558. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.558. eCollection 2022 Mar. Health Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35317418 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-451a, microRNA-34a-5p, and microRNA-221-3p as predictors of response to antidepressant treatment.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2018;51(7):e7212. doi: 10.1590/1414-431x20187212. Epub 2018 May 17. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2018. PMID: 29791588 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease: Aβ, Tau, and Epigenetic Alterations.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Apr;55(4):3021-3032. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0533-3. Epub 2017 Apr 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28456942 Review.
References
-
- Plath N, Ohana O, Dammermann B, Errington ML, Schmitz D, et al. Arc/Arg3.1 is essential for the consolidation of synaptic plasticity and memories. Neuron. 2006;52((3)):437–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

