Thioredoxin from the Indianmeal moth Plodia interpunctella: cloning and test of the allergenic potential in mice
- PMID: 22844539
- PMCID: PMC3406034
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042026
Thioredoxin from the Indianmeal moth Plodia interpunctella: cloning and test of the allergenic potential in mice
Abstract
Background/objective: The Indianmeal moth Plodia interpunctella is a highly prevalent food pest in human dwellings, and has been shown to contain a number of allergens. So far, only one of these, the arginine kinase (Plo i 1) has been identified.
Objective: The aim of this study was to identify further allergens and characterise these in comparison to Plo i 1.
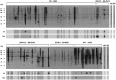
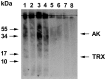
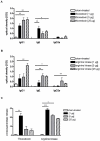
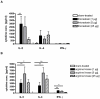
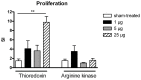
Method: A cDNA library from whole adult P. interpunctella was screened with the serum of a patient with indoor allergy and IgE to moths, and thioredoxin was identified as an IgE-binding protein. Recombinant thioredoxin was generated in E. coli, and tested together with Plo i 1 and whole moth extracts in IgE immunoblots against a large panel of indoor allergic patients' sera. BALB/c mice were immunised with recombinant thioredoxin and Plo i 1, and antibody production, mediator release from RBL cells, T-cell proliferation and cytokine production were measured.
Result: For the first time a thioredoxin from an animal species was identified as allergen. About 8% of the sera from patients with IgE against moth extracts reacted with recombinant P. interpunctella thioredoxin, compared to 25% reacting with recombinant Plo i 1. In immunised BALB/c mice, the recombinant allergens both induced classical Th2-biased immune responses such as induction IgE and IgG1 antibodies, upregulation of IL-5 and IL-4 and basophil degranulation.
Conclusion: Thioredoxin from moths like Plo i 1 acts like a classical Type I allergen as do the thioredoxins from wheat or corn. This clearly supports the pan-allergen nature of thioredoxin. The designation Plo i 2 is suggested for the new P. interpunctella allergen.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Hoffman DR (2008) Structural biology of allergens from stinging and biting insects. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 8: 338–342. - PubMed
-
- Thomas WR, Hales BJ, Smith WA (2010) House dust mite allergens in asthma and allergy. Trends Mol Med 16: 321–328. - PubMed
-
- Arruda LK, Vailes LD, Benjamin DC, Chapman MD (1995) Molecular cloning of German cockroach (Blattella germanica) allergens. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 107: 295–297. - PubMed
-
- Van Wijnen JH, Verhoeff AP, Mulder-Folkerts DK, Brachel HJ, Schou C (1997) Cockroach allergen in house dust. Allergy 52: 460–464. - PubMed
-
- Chu KH, Tang CY, Wu A, Leung PS (2005) Seafood allergy: lessons from clinical symptoms, immunological mechanisms and molecular biology. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 97: 205–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

