The complete mitochondrial genome of Galba pervia (Gastropoda: Mollusca), an intermediate host snail of Fasciola spp
- PMID: 22844544
- PMCID: PMC3406003
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042172
The complete mitochondrial genome of Galba pervia (Gastropoda: Mollusca), an intermediate host snail of Fasciola spp
Abstract
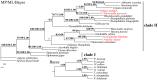
Complete mitochondrial (mt) genomes and the gene rearrangements are increasingly used as molecular markers for investigating phylogenetic relationships. Contributing to the complete mt genomes of Gastropoda, especially Pulmonata, we determined the mt genome of the freshwater snail Galba pervia, which is an important intermediate host for Fasciola spp. in China. The complete mt genome of G. pervia is 13,768 bp in length. Its genome is circular, and consists of 37 genes, including 13 genes for proteins, 2 genes for rRNA, 22 genes for tRNA. The mt gene order of G. pervia showed novel arrangement (tRNA-His, tRNA-Gly and tRNA-Tyr change positions and directions) when compared with mt genomes of Pulmonata species sequenced to date, indicating divergence among different species within the Pulmonata. A total of 3655 amino acids were deduced to encode 13 protein genes. The most frequently used amino acid is Leu (15.05%), followed by Phe (11.24%), Ser (10.76%) and IIe (8.346%). Phylogenetic analyses using the concatenated amino acid sequences of the 13 protein-coding genes, with three different computational algorithms (maximum parsimony, maximum likelihood and bayesian analysis), all revealed that the families Lymnaeidae and Planorbidae are closely related two snail families, consistent with previous classifications based on morphological and molecular studies. The complete mt genome sequence of G. pervia showed a novel gene arrangement and it represents the first sequenced high quality mt genome of the family Lymnaeidae. These novel mtDNA data provide additional genetic markers for studying the epidemiology, population genetics and phylogeographics of freshwater snails, as well as for understanding interplay between the intermediate snail hosts and the intra-mollusca stages of Fasciola spp..
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Relf V, Good B, Hanrahan JP, McCarthy E, Forbes AB, et al. (2011) Temporal studies on Fasciola hepatica in Galba truncatula in the west of Ireland. Vet Parasitol 175: 287–292. - PubMed
-
- Kaset C, Eursitthichai V, Vichasri-Grams S, Viyanant V, Grams R (2010) Rapid identification of lymnaeid snails and their infection with Fasciola gigantica in Thailand. Exp Parasitol 126: 482–488. - PubMed
-
- Zhang HY, Kraemer F, Shen YL, Gu YF, Shen T, et al. (1999) Detection of Fasciola hepatica in galba pervia by dot hybridization. Chin j vet parastiol 1: 1–3 (in Chinese).
-
- Ai L, Weng YB, Elsheikha HM, Zhao GH, Alasaad S, et al. (2011) Genetic diversity and relatedness of Fasciola spp. isolates from different hosts and geographic regions revealed by analysis of mitochondrial DNA sequences. Vet Parasitol 181: 329–334. - PubMed
-
- Alasaad S, Soriguer RC, Abu-Madi M, El Behairy A, Jowers MJ, et al. (2011) A TaqMan real-time PCR-based assay for the identification of Fasciola spp. Vet Parasitol 179: 266–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

