Simultaneous Duodenal Metal Stent Placement and EUS-Guided Choledochoduodenostomy for Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 22844572
- PMCID: PMC3404181
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl.2012.6.3.399
Simultaneous Duodenal Metal Stent Placement and EUS-Guided Choledochoduodenostomy for Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
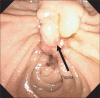
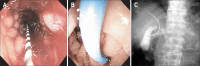
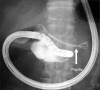
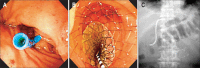
Patients with pancreatic cancer frequently suffer from both biliary and duodenal obstruction. For such patients, both biliary and duodenal self-expandable metal stent placement is necessary to palliate their symptoms, but it was difficult to cross two metal stents. Recently, endoscopic ultrasonography-guided choledochoduodenostomy (EUS-CDS) was reported to be effective for patients with an inaccessible papilla. We report two cases of pancreatic cancer with both biliary and duodenal obstructions treated successfully with simultaneous duodenal metal stent placement and EUS-CDS. The first case was a 74-year-old man with pancreatic cancer. Duodenoscopy revealed that papilla had been invaded with tumor and duodenography showed severe stenosis in the horizontal portion. After a duodenal uncovered metal stent was placed across the duodenal stricture, EUS-CDS was performed. The second case was a 63-year-old man who previously had a covered metal stent placed for malignant biliary obstruction. After removing the previously placed metal stent, EUS-CDS was performed. Then, a duodenal covered metal stent was placed across the duodenal stenosis. Both patients could tolerate a regular diet and did not suffer from stent occlusion. EUS-CDS combined with duodenal metal stent placement may be an ideal treatment strategy in patients with pancreatic cancer with both duodenal and biliary malignant obstruction.
Keywords: Duodenal stent; Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided choledochoduodenostomy; Malignant biliary obstruction.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Maetani I, Ogawa S, Hoshi H, et al. Self-expanding metal stents for palliative treatment of malignant biliary and duodenal stenoses. Endoscopy. 1994;26:701–704. - PubMed
-
- Maire F, Hammel P, Ponsot P, et al. Long-term outcome of biliary and duodenal stents in palliative treatment of patients with unresectable adenocarcinoma of the head of pancreas. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:735–742. - PubMed
-
- Maranki J, Hernandez AJ, Arslan B, et al. Interventional endoscopic ultrasound-guided cholangiography: long-term experience of an emerging alternative to percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography. Endoscopy. 2009;41:532–538. - PubMed
-
- Yamao K, Sawaki A, Takahashi K, Imaoka H, Ashida R, Mizuno N. EUS-guided choledochoduodenostomy for palliative biliary drainage in case of papillary obstruction: report of 2 cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;64:663–667. - PubMed
-
- Mutignani M, Tringali A, Shah SG, et al. Combined endoscopic stent insertion in malignant biliary and duodenal obstruction. Endoscopy. 2007;39:440–447. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

