Multiple clonal MLL fusions in a patient receiving CHOP-based chemotherapy
- PMID: 22845170
- PMCID: PMC3444640
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2012.09248.x
Multiple clonal MLL fusions in a patient receiving CHOP-based chemotherapy
Abstract
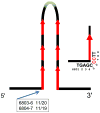
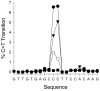
MLL rearrangements were analysed in the blood of a patient receiving chemotherapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using inverse polymerase chain reaction targeting exon 12, parallel sequencing and a custom algorithm design. Of thirteen MLL rearrangements detected, five were capable of generating MLL fusion genes, including MLL-MLLT3, the most common fusion in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML). Other fusions, all previously clinically unobserved, included MLL-NKD1, a fusion to the negative regulator of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, a pathway linked to leukaemic cell proliferation. The majority of the fusions exhibited clonal persistence from before treatment until 6 months post-chemotherapy, suggesting the fusions may confer a survival advantage to the mutant clone. MLL breakpoints were partly clustered at a specific location, indicating commonality in the process of their formation. Further, the same MLL breakpoint location exhibited a 50-100-fold increase in C to T transitions, consistent with attack by activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AICDA). As is also observed in AML and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, in this single patient setting, MLL is capable of interacting with multiple fusion partners. This finding defines a discrete site of MLL susceptibility to fragmentation, linked to possible deregulation of AICDA function.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests
Figures

References
-
- Barabe F, Kennedy JA, Hope KJ, Dick JE. Modeling the initiation and progression of human acute leukemia in mice. Science. 2007;316:600–604. - PubMed
-
- Betti CJ, Villalobos MJ, Diaz MO, Vaughan AT. Apoptotic triggers initiate translocations within the MLL gene involving the nonhomologous end joining repair system. Cancer Res. 2001;61:4550–4555. - PubMed
-
- Betti CJ, Villalobos MJ, Diaz MO, Vaughan AT. Apoptotic stimuli initiate MLL-AF9 translocations that are transcribed in cells capable of division. Cancer Res. 2003;63:1377–1381. - PubMed
-
- Broeker PL, Super HG, Thirman MJ, Pomykala H, Yonebayashi Y, Tanabe S, Zeleznik-Le N, Rowley JD. Distribution of 11q23 breakpoints within the MLL breakpoint cluster region in de novo acute leukemia and in treatment-related acute myeloid leukemia: correlation with scaffold attachment regions and topoisomerase II consensus binding sites. Blood. 1996;87:1912–1922. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

