A complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Ogura-type male-sterile cytoplasm and its comparative analysis with that of normal cytoplasm in radish (Raphanus sativus L.)
- PMID: 22846596
- PMCID: PMC3473294
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-352
A complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Ogura-type male-sterile cytoplasm and its comparative analysis with that of normal cytoplasm in radish (Raphanus sativus L.)
Abstract
Background: Plant mitochondrial genome has unique features such as large size, frequent recombination and incorporation of foreign DNA. Cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) is caused by rearrangement of the mitochondrial genome, and a novel chimeric open reading frame (ORF) created by shuffling of endogenous sequences is often responsible for CMS. The Ogura-type male-sterile cytoplasm is one of the most extensively studied cytoplasms in Brassicaceae. Although the gene orf138 has been isolated as a determinant of Ogura-type CMS, no homologous sequence to orf138 has been found in public databases. Therefore, how orf138 sequence was created is a mystery. In this study, we determined the complete nucleotide sequence of two radish mitochondrial genomes, namely, Ogura- and normal-type genomes, and analyzed them to reveal the origin of the gene orf138.
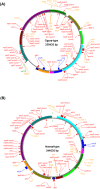
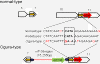
Results: Ogura- and normal-type mitochondrial genomes were assembled to 258,426-bp and 244,036-bp circular sequences, respectively. Normal-type mitochondrial genome contained 33 protein-coding and three rRNA genes, which are well conserved with the reported mitochondrial genome of rapeseed. Ogura-type genomes contained same genes and additional atp9. As for tRNA, normal-type contained 17 tRNAs, while Ogura-type contained 17 tRNAs and one additional trnfM. The gene orf138 was specific to Ogura-type mitochondrial genome, and no sequence homologous to it was found in normal-type genome. Comparative analysis of the two genomes revealed that radish mitochondrial genome consists of 11 syntenic regions (length >3 kb, similarity >99.9%). It was shown that short repeats and overlapped repeats present in the edge of syntenic regions were involved in recombination events during evolution to interconvert two types of mitochondrial genome. Ogura-type mitochondrial genome has four unique regions (2,803 bp, 1,601 bp, 451 bp and 15,255 bp in size) that are non-syntenic to normal-type genome, and the gene orf138 was found to be located at the edge of the largest unique region. Blast analysis performed to assign the unique regions showed that about 80% of the region was covered by short homologous sequences to the mitochondrial sequences of normal-type radish or other reported Brassicaceae species, although no homology was found for the remaining 20% of sequences.
Conclusions: Ogura-type mitochondrial genome was highly rearranged compared with the normal-type genome by recombination through one large repeat and multiple short repeats. The rearrangement has produced four unique regions in Ogura-type mitochondrial genome, and most of the unique regions are composed of known Brassicaceae mitochondrial sequences. This suggests that the regions unique to the Ogura-type genome were generated by integration and shuffling of pre-existing mitochondrial sequences during the evolution of Brassicaceae, and novel genes such as orf138 could have been created by the shuffling process of mitochondrial genome.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Complete mitochondrial genome sequence and identification of a candidate gene responsible for cytoplasmic male sterility in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) containing DCGMS cytoplasm.Theor Appl Genet. 2013 Jul;126(7):1763-74. doi: 10.1007/s00122-013-2090-0. Epub 2013 Mar 29. Theor Appl Genet. 2013. PMID: 23539087
-
Cytoplasmic suppression of Ogura cytoplasmic male sterility in European natural populations of Raphanus raphanistrum.Theor Appl Genet. 2007 May;114(8):1333-43. doi: 10.1007/s00122-007-0520-6. Epub 2007 Feb 23. Theor Appl Genet. 2007. PMID: 17318491
-
Organelle Comparative Genome Analysis Reveals Novel Alloplasmic Male Sterility with orf112 in Brassica oleracea L.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 8;22(24):13230. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413230. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948024 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic male sterility in Brassicaceae crops.Breed Sci. 2014 May;64(1):38-47. doi: 10.1270/jsbbs.64.38. Breed Sci. 2014. PMID: 24987289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant mitochondrial DNA.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2017 Jan 1;22(6):1023-1032. doi: 10.2741/4531. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2017. PMID: 27814661 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of six novel ORFs in the plastome of Mankyua chejuense and phylogeny of eusporangiate ferns.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 7;8(1):16466. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34825-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30405200 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating Mitochondrial DNA Markers of Ogura-Based CMS Lines in Indian Cauliflowers (Brassica oleracea var. botrytis L.) and Their Floral Abnormalities Due to Diversity in Cytonuclear Interactions.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Apr 30;12:631489. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.631489. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33995434 Free PMC article.
-
Organelle genome composition and candidate gene identification for Nsa cytoplasmic male sterility in Brassica napus.BMC Genomics. 2019 Nov 6;20(1):813. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6187-y. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31694534 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial genome rearrangements in glomus species triggered by homologous recombination between distinct mtDNA haplotypes.Genome Biol Evol. 2013;5(9):1628-43. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evt120. Genome Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 23925788 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial genome and transcriptome analysis of five alloplasmic male-sterile lines in Brassica juncea.BMC Genomics. 2019 May 8;20(1):348. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5721-2. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31068124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palmer JD, Herbo LA. Unicircular structure of the Brassica hirta mitochondrial genome. Curr Genet. 1987;11(6–7):565–570. - PubMed
-
- Schnable PS, Wise RP. The molecular basis of cytoplasmic male sterility and fertility restoration. Trends Plant Sci. 1998;3(5):175–180. doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(98)01235-7. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

