Construction of a stability landscape of the CH3 domain of human IgG1 by combining directed evolution with high throughput sequencing
- PMID: 22846908
- PMCID: PMC3469823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.07.017
Construction of a stability landscape of the CH3 domain of human IgG1 by combining directed evolution with high throughput sequencing
Abstract
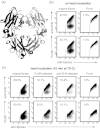
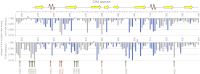
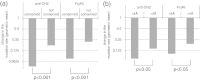
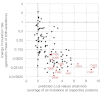
One of the most important but still poorly understood issues in protein chemistry is the relationship between sequence and stability of proteins. Here, we present a method for analyzing the influence of each individual residue on the foldability and stability of an entire protein. A randomly mutated library of the crystallizable fragment of human immunoglobulin G class 1 (IgG1-Fc) was expressed on the surface of yeast, followed by heat incubation at 79°C and selection of stable variants that still bound to structurally specific ligands. High throughput sequencing allowed comparison of the mutation rate between the starting and selected library pools, enabling the generation of a stability landscape for the entire CH3 domain of human IgG1 at single residue resolution. Its quality was analyzed with respect to (i) the structure of IgG1-Fc, (ii) evolutionarily conserved positions and (iii) in silico calculations of the energy of unfolding of all variants in comparison with the wild-type protein. In addition, this new experimental approach allowed the assignment of functional epitopes of structurally specific ligands used for selection [Fc γ-receptor I (CD64) and anti-human CH2 domain antibody] to distinct binding regions in the CH2 domain.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- McCafferty J., Griffiths A.D., Winter G., Chiswell D.J. Phage antibodies: filamentous phage displaying antibody variable domains. Nature. 1990;348:552–554. - PubMed
-
- Smith G.P. Filamentous fusion phage: novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science. 1985;228:1315–1317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

