Galectin-3 protein regulates mobility of N-cadherin and GM1 ganglioside at cell-cell junctions of mammary carcinoma cells
- PMID: 22846995
- PMCID: PMC3463368
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.353334
Galectin-3 protein regulates mobility of N-cadherin and GM1 ganglioside at cell-cell junctions of mammary carcinoma cells
Abstract
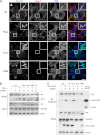
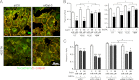
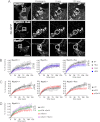
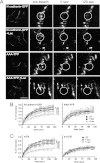
Galectin-3 binding to cell surface glycoproteins, including branched N-glycans generated by N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V (Mgat5) activity, forms a multivalent, heterogeneous, and dynamic lattice. This lattice has been shown to regulate integrin and receptor tyrosine kinase signaling promoting tumor cell migration. N-cadherin is a homotypic cell-cell adhesion receptor commonly overexpressed in tumor cells that contributes to cell motility. Here we show that galectin-3 and N-cadherin interact and colocalize with the lipid raft marker GM1 ganglioside in cell-cell junctions of mammary epithelial cancer cells. Disruption of the lattice by deletion of Mgat5, siRNA depletion of galectin-3, or competitive inhibition with lactose stabilizes cell-cell junctions. It also reduces, in a p120-catenin-dependent manner, the dynamic pool of junctional N-cadherin. Proteomic analysis of detergent-resistant membranes (DRMs) revealed that the galectin lattice opposes entry of many proteins into DRM rafts. N-cadherin and catenins are present in DRMs; however, their DRM distribution is not significantly affected by lattice disruption. Galectin lattice integrity increases the mobile fraction of the raft marker, GM1 ganglioside binding cholera toxin B subunit Ctb, at cell-cell contacts in a p120-catenin-independent manner, but does not affect the mobility of either Ctb-labeled GM1 or GFP-coupled N-cadherin in nonjunctional regions. Our results suggest that the galectin lattice independently enhances lateral molecular diffusion by direct interaction with specific glycoconjugates within the adherens junction. By promoting exchange between raft and non-raft microdomains as well as molecular dynamics within junction-specific raft microdomains, the lattice may enhance turnover of N-cadherin and other glycoconjugates that determine junctional stability and rates of cell migration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Galectin-3- and phospho-caveolin-1-dependent outside-in integrin signaling mediates the EGF motogenic response in mammary cancer cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Jul;24(13):2134-45. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-02-0095. Epub 2013 May 8. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23657817 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin binding to Mgat5-modified N-glycans regulates fibronectin matrix remodeling in tumor cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;26(8):3181-93. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.8.3181-3193.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16581792 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the distinct distributions of VE- and N-cadherins in endothelial cells: a key role for p120-catenin.Exp Cell Res. 2010 Oct 1;316(16):2587-99. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.06.015. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Exp Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 20599949
-
Cadherins and the mammary gland.J Cell Biochem. 2005 Jun 1;95(3):488-96. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20419. J Cell Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15838893 Review.
-
Dynamic Regulation of Vascular Permeability by Vascular Endothelial Cadherin-Mediated Endothelial Cell-Cell Junctions.J Nippon Med Sch. 2017;84(4):148-159. doi: 10.1272/jnms.84.148. J Nippon Med Sch. 2017. PMID: 28978894 Review.
Cited by
-
Galectin-3 enhances angiogenic and migratory potential of microglial cells via modulation of integrin linked kinase signaling.Brain Res. 2013 Feb 16;1496:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.12.008. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23246924 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Transmembrane Signaling by Phase Separation.Annu Rev Biophys. 2019 May 6;48:465-494. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-052118-115534. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Annu Rev Biophys. 2019. PMID: 30951647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Identification and mRNA Expression Profiles of Galectin-9 Gene in Red Sea Bream (Pagrus major) Infected with Pathogens.Animals (Basel). 2021 Jan 11;11(1):139. doi: 10.3390/ani11010139. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33440635 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 Release in the Bone Marrow Microenvironment Promotes Drug Resistance and Relapse in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Life (Basel). 2025 Jun 10;15(6):937. doi: 10.3390/life15060937. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40566589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galectin-3-Insights from Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 25;26(13):6101. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136101. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649879 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad N., Gabius H. J., André S., Kaltner H., Sabesan S., Roy R., Liu B., Macaluso F., Brewer C. F. (2004) Galectin-3 precipitates as a pentamer with synthetic multivalent carbohydrates and forms heterogeneous cross-linked complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 10841–10847 - PubMed
-
- Mehul B., Bawumia S., Hughes R. C. (1995) Cross-linking of galectin 3, a galactose-binding protein of mammalian cells, by tissue-type transglutaminase. FEBS Lett. 360, 160–164 - PubMed
-
- Nieminen J., Kuno A., Hirabayashi J., Sato S. (2007) Visualization of galectin-3 oligomerization on the surface of neutrophils and endothelial cells using fluorescence resonance energy transfer. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 1374–1383 - PubMed
-
- Lau K. S., Partridge E. A., Grigorian A., Silvescu C. I., Reinhold V. N., Demetriou M., Dennis J. W. (2007) Complex N-glycan number and degree of branching cooperate to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. Cell 129, 123–134 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

