Lipemia retinalis - an unusual cause of visual acuity deterioration
- PMID: 22847206
- PMCID: PMC3560707
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.883257
Lipemia retinalis - an unusual cause of visual acuity deterioration
Abstract
Background: Hyperlipidemia is an identified factor of premature vessel atherosclerosis. Lipemia retinalis is an unusual retinal manifestation of hyperlipidemia and is thought to be directly correlated with the serum triglyceride level.
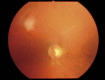
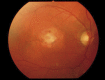
Case report: This paper discusses the case of a 55-year-old patient with lipemia retinalis, which deteriorated his visual acuity. The patient had an extremely high serum cholesterol level (1053 mg/dl) and a very high level of triglycerides (1513 mg/dl). The normalization of serum lipids, reversion of retinal vessels alterations and visual acuity improvement was achieved after an intensive statin lipid-lowering therapy. Pathological changes of the patient's retina, connected with lipemia retinalis, disappeared completely.
Conclusions: Hyperlipidemia can cause lipemia retinalis, which is characterized by the hyperlipidemic vascular lesions-whitish color of vessels, lipid infiltration into the retina and decrease of visual acuity. The lipid-lowering therapy may lead to the normalization of the appearance of the fundus and restore the visual acuity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Improved visual function with dietary intervention in a child with lipemia retinalis.J AAPOS. 2014 Oct;18(5):488-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jaapos.2014.05.004. Epub 2014 Oct 21. J AAPOS. 2014. PMID: 25439305
-
Lipemia retinalis following FLAG-Ida protocol in an 11-year-old patient with acute myeloid leukemia.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2025 Jan;35(1):NP5-NP9. doi: 10.1177/11206721241287347. Epub 2024 Sep 28. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39340315
-
Case Report: Swept-source Optical Coherence Tomography and Angiography Findings in Lipemia Retinalis.Optom Vis Sci. 2022 Jan 1;99(1):76-81. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000001830. Optom Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 34882611
-
The effect of statins on postprandial lipemia.Curr Drug Targets. 2007 Apr;8(4):551-60. doi: 10.2174/138945007780362809. Curr Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17430126 Review.
-
2017 Taiwan lipid guidelines for high risk patients.J Formos Med Assoc. 2017 Apr;116(4):217-248. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2016.11.013. Epub 2017 Feb 24. J Formos Med Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28242176 Review.
Cited by
-
Incidental finding of lipaemia retinalis on diabetic retinal screening.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2021 Oct 1;2021:21-0051. doi: 10.1530/EDM-21-0051. Online ahead of print. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34673543 Free PMC article.
-
Statin therapy decreased the recurrence frequency of atrial fibrillation after electrical cardioversion: a meta-analysis.Med Sci Monit. 2014 Dec 21;20:2753-8. doi: 10.12659/MSM.891049. Med Sci Monit. 2014. PMID: 25529758 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal thickness and fundus blood flow density changes in chest pain subjects with dyslipidemia.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Nov 18;16(11):1860-1866. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.11.19. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 38028521 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms Underlying Early-Stage Changes in Visual Performance and Retina Function After Experimental Induction of Sustained Dyslipidemia.Neurochem Res. 2018 Aug;43(8):1500-1510. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2563-2. Epub 2018 Jun 2. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 29860619 Free PMC article.
-
Vasoregression: A Shared Vascular Pathology Underlying Macrovascular And Microvascular Pathologies?OMICS. 2015 Dec;19(12):733-53. doi: 10.1089/omi.2015.0128. OMICS. 2015. PMID: 26669709 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leaf DA. Chylomicronemia and the chylomicronemia syndrome: a practical approach to management. Am J Med. 2008;121:10–12. - PubMed
-
- Nagra PK, Ho AC, Dugan JD. Lipemia retinalis associated with branch retinal vein occlusion. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003;135:539–42. - PubMed
-
- Park YH, Lee YC. Images in clinical medicine. Lipemia retinalis associated with secondary hyperlipidemia. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(10):e11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

