Prevalence, incidence, and demographics of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis from 2000 to 2004 among children in the US Medicaid beneficiary population
- PMID: 22847366
- PMCID: PMC3564552
- DOI: 10.1002/art.34472
Prevalence, incidence, and demographics of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis from 2000 to 2004 among children in the US Medicaid beneficiary population
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the nationwide prevalence, incidence, and sociodemographics of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis among children in the US Medicaid beneficiary population.
Methods: Children ages 3 years to <18 years with a diagnosis of SLE (defined as ≥3 claims with an International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision [ICD-9] code of 710.0 for SLE, each >30 days apart) were identified from the US Medicaid Analytic eXtract database from 2000 to 2004. This database contains all inpatient and outpatient Medicaid claims for 47 US states and the District of Columbia. Lupus nephritis was identified from ≥2 ICD-9 billing codes for glomerulonephritis, proteinuria, or renal failure, each recorded >30 days apart. The prevalence and incidence of SLE and lupus nephritis were calculated among Medicaid-enrolled children overall and within sociodemographic groups.
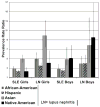
Results: Of the 30,420,597 Medicaid-enrolled children during these years, 2,959 were identified as having SLE. The prevalence of SLE was 9.73 (95% confidence interval [95% CI] 9.38-10.08) per 100,000 Medicaid-enrolled children. Among the children with SLE, 84% were female, 40% were African American, 25% were Hispanic, 21% were White, and 42% resided in the South region of the US. Moreover, of the children with SLE, 1,106 (37%) had lupus nephritis, representing a prevalence of 3.64 (95% CI 3.43-3.86) per 100,000 children. The average annual incidence of SLE was 2.22 cases (95% CI 2.05-2.40) and that of lupus nephritis was 0.72 cases (95% CI 0.63-0.83) per 100,000 Medicaid enrollees per year. The prevalence and incidence rates of SLE and lupus nephritis increased with age, were higher in girls than in boys, and were higher in all non-White racial/ethnic groups.
Conclusion: In the current study, the prevalence and incidence rates of SLE among Medicaid-enrolled children in the US are high compared to studies in other populations. In addition, these data represent the first population-based estimates of the prevalence and incidence of lupus nephritis in the US to date.
Copyright © 2012 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Brunner HI, Gladman DD, Ibanez D, Urowitz MD, Silverman ED. Difference in disease features between childhood-onset and adult-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(2):556–62. - PubMed
-
- Al Salloum AA. Lupus nephritis in childhood. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2003;14(1):43–56. - PubMed
-
- Cameron JS. Lupus nephritis in childhood and adolescence. Pediatr Nephrol. 1994;8(2):230–49. - PubMed
-
- Padovan M, Govoni M, Castellino G, Rizzo N, Fotinidi M, Trotta F. Late onset systemic lupus erythematosus: no substantial differences using different cut-off ages. Rheumatol Int. 2007;27(8):735–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical