Diurnal expression of Dnmt3b mRNA in mouse liver is regulated by feeding and hepatic clockwork
- PMID: 22847467
- PMCID: PMC3515014
- DOI: 10.4161/epi.21539
Diurnal expression of Dnmt3b mRNA in mouse liver is regulated by feeding and hepatic clockwork
Abstract
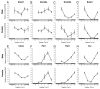
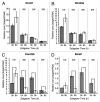
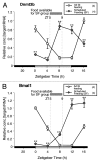
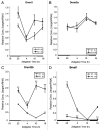
DNA methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) is critically involved in de novo DNA methylation and genomic stability, while the regulatory mechanism in liver is largely unknown. We previously reported that diurnal variation occurs in the mRNA expression of Dnmt3b in adult mouse liver. The aim of this study was to determine the mechanism underlying the diurnal expression pattern. The highest level and the lowest level of Dnmt3b mRNA expression were confirmed to occur at dawn and in the afternoon, respectively, and the expression pattern of Dnmt3b closely coincided with that of Bmal1. Since the diurnal pattern of Dnmt3b mRNA expression developed at weaning and scheduled feeding to separate the feeding cycle from the light/dark cycle led to a phase-shift in the expression, it could be assumed that feeding plays a critical role as an entrainment signal. In liver-specific Bmal1 knockout (L-Bmal1 KO) mice, L-Bmal1 deficiency resulted in significantly higher levels of Dnmt3b at all measured time points, and the time when the expression was the lowest in wild-type mice was shifted to earlier. Investigation of global DNA methylation revealed a temporal decrease of 5-methyl-cytosine percentage in the genome of wild-type mice in late afternoon. By contrast, no such decrease in 5-methyl-cytosine percentage was detected in L-Bmal1 KO mice, suggesting that altered Dnmt3b expression affects the DNA methylation state. Taken together, the results suggest that the feeding and hepatic clockwork generated by the clock genes, including Bmal1, regulate the diurnal variation in Dnmt3b mRNA expression and the consequent dynamic changes in global DNA methylation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional regulatory logic of the diurnal cycle in the mouse liver.PLoS Biol. 2017 Apr 17;15(4):e2001069. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2001069. eCollection 2017 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2017. PMID: 28414715 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide and phase-specific DNA-binding rhythms of BMAL1 control circadian output functions in mouse liver.PLoS Biol. 2011 Feb;9(2):e1000595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000595. Epub 2011 Feb 22. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21364973 Free PMC article.
-
Clock gene Bmal1 controls diurnal rhythms in expression and activity of intestinal carboxylesterase 1.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;73(1):52-59. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgaa035. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33791812
-
Resetting process of peripheral circadian gene expression after the combined reversal of feeding schedule and light/dark cycle via a 24-h light period transition in rats.Physiol Res. 2010;59(4):581-590. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.931818. Epub 2009 Nov 20. Physiol Res. 2010. PMID: 19929146
-
Methyltransferase DNMT3B in leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2020 Feb;61(2):263-273. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2019.1666377. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Leuk Lymphoma. 2020. PMID: 31547729 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Circadian Clocks and Its Involvement in Drug Addiction.Genes (Basel). 2021 Aug 19;12(8):1263. doi: 10.3390/genes12081263. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and epigenomic mechanisms of mammalian circadian transcription.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016 Dec 6;23(12):1045-1052. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3324. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27922611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combinatorial regulation of hepatic cytoplasmic signaling and nuclear transcriptional events by the OGT/REV-ERBα complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 20;115(47):E11033-E11042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1805397115. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30397120 Free PMC article.
-
Daily variation in global and local DNA methylation in mouse livers.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 17;10(2):e0118101. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118101. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25689298 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic nature of DNA methylation: a role in response to social and seasonal variation.Integr Comp Biol. 2014 Jul;54(1):68-76. doi: 10.1093/icb/icu034. Epub 2014 May 10. Integr Comp Biol. 2014. PMID: 24813708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Geiman TM, Muegge K. DNA methylation in early development. Mol Reprod Dev. 2010;77:105–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
