A phase I trial and pharmacokinetic study of a 24-hour infusion of trabectedin (Yondelis®, ET-743) in children and adolescents with relapsed or refractory solid tumors
- PMID: 22847981
- PMCID: PMC3442122
- DOI: 10.1002/pbc.24201
A phase I trial and pharmacokinetic study of a 24-hour infusion of trabectedin (Yondelis®, ET-743) in children and adolescents with relapsed or refractory solid tumors
Abstract
Background: The objectives of this phase I study were to determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD), toxicity profile, and pharmacokinetics of a 24-hour continuous intravenous infusion of trabectedin administered to children and adolescents with refractory or relapsed solid tumors.
Procedure: Patients between the ages of 4 and 16 years old with refractory solid tumors received trabectedin as a 24-hour infusion every 21 days. Dexamethasone and prophylactic growth factor support were administered with each cycle. Pharmacokinetic studies were conducted during cycle 1.
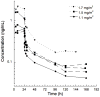
Results: Patients (n = 12) median (range) age 14.5 (8-16) years received trabectedin at 1.1 (n = 3), 1.5 (n = 6), or 1.7 (n = 3) mg/m(2). At the 1.5 mg/m(2) dose level, one patient had dose limiting anorexia and fatigue. At 1.7 mg/m(2), two patients experienced dose limiting toxicity, dehydration, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase elevation. Non-dose limiting toxicities included elevated serum transaminases, myelosuppression, nausea, emesis, and fatigue. Plasma pharmacokinetic parameters were similar to historical data in adults. One partial response was observed in a patient with neuroendocrine carcinoma. Stable disease (≥6 cycles) was achieved in three patients (osteosarcoma n = 2, desmoplastic small round cell tumor n = 1).
Conclusions: The MTD of trabectedin in pediatric patients with refractory solid tumors is 1.5 mg/m(2) IV over 24 hours every 21 days. Dexamethasone to ameliorate hepatic toxicity and prophylactic growth factor support are required.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: Authors PZ and EB are employed by Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical R&D, LLC
Similar articles
-
Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of trabectedin as a 1- or 3-hour infusion weekly in patients with advanced solid malignancies.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 May 15;15(10):3591-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2889. Epub 2009 May 5. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19417019 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of Yondelis (Ecteinascidin-743; ET-743) administered as an infusion over 1 h or 3 h every 21 days in patients with solid tumours.Eur J Cancer. 2003 Sep;39(13):1842-51. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(03)00458-1. Eur J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12932661 Clinical Trial.
-
Mechanism-based pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic meta-analysis of trabectedin (ET-743, Yondelis) induced neutropenia.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008 Jan;83(1):130-43. doi: 10.1038/sj.clpt.6100259. Epub 2007 Jun 27. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008. PMID: 17597713
-
Trabectedin: Ecteinascidin 743, Ecteinascidin-743, ET 743, ET-743, NSC 684766.Drugs R D. 2006;7(5):317-28. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200607050-00005. Drugs R D. 2006. PMID: 16922593 Review.
-
Trabectedin: a review of its use in soft tissue sarcoma and ovarian cancer.Drugs. 2010 Feb 12;70(3):355-76. doi: 10.2165/11202860-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20166769 Review.
Cited by
-
Trabectedin for desmoplastic small round cell tumours: a possible treatment option?Clin Sarcoma Res. 2014 Apr 25;4:3. doi: 10.1186/2045-3329-4-3. eCollection 2014. Clin Sarcoma Res. 2014. PMID: 24829745 Free PMC article.
-
Starvation tactics using natural compounds for advanced cancers: pharmacodynamics, clinical efficacy, and predictive biomarkers.Cancer Med. 2018 Jun;7(6):2221-2246. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1467. Epub 2018 May 6. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 29732738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trabectedin and Eribulin: Where Do They Fit in the Management of Soft Tissue Sarcoma?Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017 Jun;18(6):34. doi: 10.1007/s11864-017-0477-x. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28534249 Review.
-
Desmoplastic small round cell tumors: Multimodality treatment and new risk factors.Cancer Med. 2019 Feb;8(2):527-542. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1940. Epub 2019 Jan 16. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 30652419 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Systematic review of phase-I/II trials enrolling refractory and recurrent Ewing sarcoma: Actual knowledge and future directions to optimize the research.Cancer Med. 2021 Mar;10(5):1589-1604. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3712. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33452711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martinez EJ, Corey EJ. A new, more efficient, and effective process for the synthesis of a key pentacyclic intermediate for production of ecteinascidin and phthalascidin antitumor agents. Org Lett. 2000;2:993–996. - PubMed
-
- Pommier Y, Kohlhagen G, Bailly C, Waring M, Mazumder A, Kohn KW. DNA sequence- and structure-selective alkylation of guanine N2 in the DNA minor groove by ecteinascidin 743, a potent antitumor compound from the Caribbean tunicate Ecteinascidia turbinata. Biochemistry. 1996;35:13303–13309. - PubMed
-
- Friedman D, Hu Z, Kolb EA, Gorfajn B, Scotto KW. Ecteinascidin-743 inhibits activated but not constitutive transcription. Cancer Res. 2002;62:3377–3381. - PubMed
-
- Takebayashi Y, Pourquier P, Zimonjic DB, et al. Antiproliferative activity of ecteinascidin 743 is dependent upon transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair. Nat Med. 2001;7:961–966. - PubMed
-
- Tavecchio M, Simone M, Erba E, et al. Role of homologous recombination in trabectedin-induced DNA damage. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44:609–618. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources