Targeting subcellular localization through the polo-box domain: non-ATP competitive inhibitors recapitulate a PLK1 phenotype
- PMID: 22848093
- PMCID: PMC3711794
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0006-T
Targeting subcellular localization through the polo-box domain: non-ATP competitive inhibitors recapitulate a PLK1 phenotype
Abstract
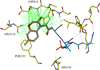
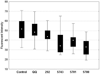
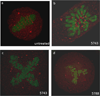
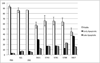
The polo-box domain (PBD) has critical roles in the mitotic functions of polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1). The replacement with partial ligand alternative through computational enrichment (REPLACE) strategy to develop inhibitors of protein-protein interactions has identified alternatives for the N-terminal tripeptide of a Cdc25C substrate. In addition, a peptide structure-activity relationship described key determinants and novel information useful for drug design. Fragment-ligated inhibitory peptides (FLIP) were generated with comparable affinity to peptide PBD inhibitors and possessed antiproliferative phenotypes in cells consistent with the observed decrease in PLK1 centrosomal localization. These FLIPs showed evidence of enhanced PLK1 inhibition in cells relative to peptides and induced monopolar and multipolar spindles, which stands in contrast to previously reported small-molecule PBD inhibitors that display phenotypes only partially representative of PLK1 knockdown. Progress obtained applying REPLACE validates this approach for identifying fragment alternatives for determinants of the Cdc25C-binding motif and extends its applicability of the strategy for discovering protein-protein interaction inhibitors. In addition, the described PBD inhibitors retain high specificity for PLK1 over PLK3 and therefore show promise as isotype selective, non-ATP competitive kinase inhibitors that provide new impetus for the development of PLK1-selective antitumor therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Xie S, Xie B, Lee MY, Dai W. Regulation of cell cycle checkpoints by polo-like kinases. Oncogene. 2005;24:277–286. - PubMed
-
- McInnes C, Wyatt MD. PLK1 as an oncology target: current status and future potential. Drug Discov Today. 2011;16:619–625. - PubMed
-
- Wolf G, Elez R, Doermer A, Holtrich U, Ackermann H, Stutte HJ, et al. Prognostic significance of polo-like kinase (PLK) expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 1997;14:543–549. - PubMed
-
- Tokumitsu Y, Mori M, Tanaka S, Akazawa K, Nakano S, Niho Y. Prognostic significance of polo-like kinase expression in esophageal carcinoma. International Journal of Oncology. 1999;15:687–692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

