Molecular and microscopic analysis of bacteria and viruses in exhaled breath collected using a simple impaction and condensing method
- PMID: 22848436
- PMCID: PMC3405091
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041137
Molecular and microscopic analysis of bacteria and viruses in exhaled breath collected using a simple impaction and condensing method
Abstract
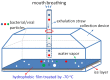
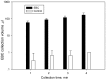
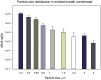
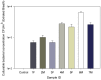
Exhaled breath condensate (EBC) is increasingly being used as a non-invasive method for disease diagnosis and environmental exposure assessment. By using hydrophobic surface, ice, and droplet scavenging, a simple impaction and condensing based collection method is reported here. Human subjects were recruited to exhale toward the device for 1, 2, 3, and 4 min. The exhaled breath quickly formed into tiny droplets on the hydrophobic surface, which were subsequently scavenged into a 10 µL rolling deionized water droplet. The collected EBC was further analyzed using culturing, DNA stain, Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and colorimetry (VITEK 2) for bacteria and viruses.Experimental data revealed that bacteria and viruses in EBC can be rapidly collected using the method developed here, with an observed efficiency of 100 µL EBC within 1 min. Culturing, DNA stain, SEM, and qPCR methods all detected high bacterial concentrations up to 7000 CFU/m(3) in exhaled breath, including both viable and dead cells of various types. Sphingomonas paucimobilis and Kocuria variants were found dominant in EBC samples using VITEK 2 system. SEM images revealed that most bacteria in exhaled breath are detected in the size range of 0.5-1.0 µm, which is able to enable them to remain airborne for a longer time, thus presenting a risk for airborne transmission of potential diseases. Using qPCR, influenza A H3N2 viruses were also detected in one EBC sample. Different from other devices restricted solely to condensation, the developed method can be easily achieved both by impaction and condensation in a laboratory and could impact current practice of EBC collection. Nonetheless, the reported work is a proof-of-concept demonstration, and its performance in non-invasive disease diagnosis such as bacterimia and virus infections needs to be further validated including effects of its influencing matrix.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

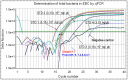
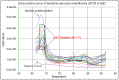

References
-
- Douwes J, Thorne P, Pearce N, Heederik D. Bioaerosol health effects and exposure assessment: Progress and prospects. Ann Occup Hyg. 2003;3:187–200. - PubMed
-
- Xu Z, Wu Y, Shen F, Chen Q, Tan M, et al. Bioaerosol science, technology, and engineering: past, present, and future. Aerosol Sci Technol. 2011;45:1337–1349.
-
- Couch R, Knight V, Gerone P, Cate T, Douglas R. Factors influencing response of volunteers to inoculation with Coxsackie virus A type 21. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969;99:24–30. - PubMed
-
- Loosli C, Hertweck M, Hockwald R. Airborne influenza PR8-A virus infections in actively immunized mice. Arch Envir Hlth. 1970;21:332–346. - PubMed
-
- Knight V. Hers JF, Winkles KC, editors. Airborne transmission and pulmonary deposition of respiratory viruses. 1973. pp. 175–182. Airborne transmission and airborne infections. VIth Int. Symp. on Aerobiology. New York, NY: Wiley, pp.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

