Long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids alter oxytocin signaling and receptor density in cultured pregnant human myometrial smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 22848573
- PMCID: PMC3406084
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041708
Long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids alter oxytocin signaling and receptor density in cultured pregnant human myometrial smooth muscle cells
Abstract
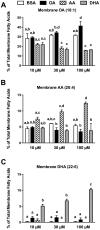
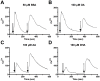
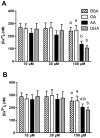
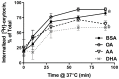
Epidemiological studies and interventional clinical trials indicate that consumption of long chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC n-3 PUFA) such as docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) lengthen gestational duration. Although the mechanisms are not well understood, prostaglandins (PG) of the 2-series are known to play a role in the initiation and progress of labor. In animal studies, modest DHA provision has been shown to reduce placental and uterine PGE(2) and PGF(2α), matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 expression, and placental collagenase activity. However, modulation of PG biosynthesis may not account for all the effects of LC n-3 PUFAs in labor. We investigated one potential PG-independent mechanism of LC PUFA action using cultured pregnant human myometrial smooth muscle cells. Our goal was to characterize the effect of LC PUFA treatment on oxytocin signaling, a potent uterotonic hormone involved in labor. The addition of 10 µM-100 µM DHA or arachidonic acid (AA) to the culture media for 48 h resulted in dose dependent enrichment of these fatty acids in membrane lipid. DHA and AA significantly inhibited phosphatidylinositol turnover and [Ca(2+)](i) mobilization with oxytocin stimulation compared to bovine serum albumin control and equimolar oleic acid. DHA and AA significantly reduced oxytocin receptor membrane concentration without altering binding affinity or rate of receptor internalization. These findings demonstrate a role for LC n-3 PUFAs in regulation of oxytocin signaling and provide new insight into additional mechanisms pertaining to reports of dietary fish and fish oil consumption prolonging gestation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alteration of prostaglandin production and agonist responsiveness by n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in endometrial cells from late-gestation ewes.J Endocrinol. 2004 Aug;182(2):249-56. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1820249. J Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15283685
-
Oxytocin signaling in human myometrium is impaired by prolonged exposure to interleukin-1.Biol Reprod. 2000 Sep;63(3):846-50. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod63.3.846. Biol Reprod. 2000. PMID: 10952930
-
Regulation of oxytocin receptor responsiveness by G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 in human myometrial smooth muscle.Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Aug;23(8):1272-80. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0047. Epub 2009 May 7. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19423652 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemistry of myometrial contractility.Baillieres Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 1992 Dec;6(4):755-69. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3552(05)80187-7. Baillieres Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 1992. PMID: 1335853 Review.
-
Myometrial oxytocin receptor expression and intracellular pathways.Minerva Ginecol. 2014 Jun;66(3):267-80. Minerva Ginecol. 2014. PMID: 24971782 Review.
Cited by
-
Female infertility and diet, is there a role for a personalized nutritional approach in assisted reproductive technologies? A Narrative Review.Front Nutr. 2022 Jul 22;9:927972. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.927972. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35938101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Constitutive activation of transforming growth factor Beta receptor 1 in the mouse uterus impairs uterine morphology and function.Biol Reprod. 2015 Feb;92(2):34. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.114.125146. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Biol Reprod. 2015. PMID: 25505200 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty Acid Metabolism Disruptions: A Subtle yet Critical Factor in Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Nov 4;20(15):6018-6037. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.103404. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39664564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Herbal Bioactive Compounds on the Angiogenic Factors and Modulation of Inflammatory Mediators in the Patients with the Deep Second-Degree Burn: A Single-Blinded, Randomized Clinical Trial.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2025 Jan 28;39:16. doi: 10.47176/mjiri.39.16. eCollection 2025. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2025. PMID: 40486016 Free PMC article.
-
CD38/cADPR-mediated calcium signaling in a human myometrial smooth muscle cell line, PHM1.IUBMB Life. 2024 Dec;76(12):1223-1233. doi: 10.1002/iub.2904. Epub 2024 Aug 12. IUBMB Life. 2024. PMID: 39135342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamilton BE, Martin JA, Ventura SJ (2011) Births: preliminary data for 2010. Natl Vital Stat Rep 60 (2):1–36. - PubMed
-
- Davidoff MJ, Dias T, Damus K, Russell R, Bettegowda VR, et al. (2006) Changes in the gestational age distribution among U.S. singleton births: impact on rates of late preterm birth, 1992 to 2002. Semin Perinatol 30 (1):8–15. - PubMed
-
- McCormick MC (1985) The contribution of low birth weight to infant mortality and childhood morbidity. N Engl J Med 312 (2):82–90. - PubMed
-
- Kramer MS, Demissie K, Yang H, Platt RW, Sauve R, et al. (2000) The contribution of mild and moderate preterm birth to infant mortality. Fetal and Infant Health Study Group of the Canadian Perinatal Surveillance System. Jama 284 (7):843–849. - PubMed
-
- Allen KG, Harris MA (2001) The role of n-3 fatty acids in gestation and parturition. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 226 (6):498–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

