ExoU activates NF-κB and increases IL-8/KC secretion during Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
- PMID: 22848596
- PMCID: PMC3406076
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041772
ExoU activates NF-κB and increases IL-8/KC secretion during Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
Abstract
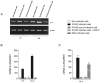
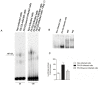
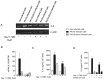
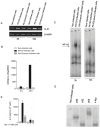
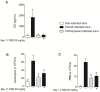
ExoU, a Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin injected into host cytosol by type III secretion system, exhibits a potent proinflammatory activity that leads to a marked recruitment of neutrophils to infected tissues. To evaluate the mechanisms that account for neutrophil infiltration, we investigated the effect of ExoU on IL-8 secretion and NF-κB activation. We demonstrate that ExoU increases IL-8 mRNA and protein levels in P. aeruginosa-infected epithelial and endothelial cell lines. Also, ExoU induces the nuclear translocation of p65/p50 NF-κB transactivator heterodimer as well as NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activity. ChIP assays clearly revealed that ExoU promotes p65 binding to NF-κB site in IL-8 promoter and the treatment of cultures with the NF-κB inhibitor Bay 11-7082 led to a significant reduction in IL-8 mRNA levels and protein secretion induced by ExoU. These results were corroborated in a murine model of pneumonia that revealed a significant reduction in KC secretion and neutrophil infiltration in bronchoalveolar lavage when mice were treated with Bay 11-7082 before infection with an ExoU-producing strain. In conclusion, our data demonstrate that ExoU activates NF-κB, stimulating IL-8 expression and secretion during P. aeruginosa infection, and unveils a new mechanism triggered by this important virulence factor to interfere in host signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
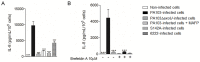

References
-
- Schulert GS, Feltman H, Rabin SDP, Martin CG, Battle SE, et al. Secretion of the toxin ExoU is a marker for highly virulent Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates obtained from patients with hospital-acquired pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 2003;188:1695–1706. - PubMed
-
- Wareham DW, Curtis MA. A genotypic and phenotypic comparison of type III secretion profiles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis and bacteremia isolates. Int J Med Microbiol. 2007;297:227–234. - PubMed
-
- Engel J, Balachandran P. Role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III effectors in disease. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2009;12:61–66. - PubMed
-
- Saliba AM, Nascimento DO, Silva MCA, Assis MC, Gayer CRM, et al. Eicosanoid-mediated proinflammatory activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExoU. Cell.Microbiol. 2005;7:1811–1822. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann E, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Holtmann H, Kracht M. Multiple control of interleukin-8 gene expression. J Leukoc Biol. 2002;72:847–855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

