PGC-1α is dispensable for exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 22848618
- PMCID: PMC3404101
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041817
PGC-1α is dispensable for exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle
Abstract
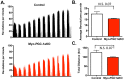
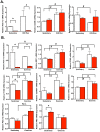
Exercise confers numerous health benefits, many of which are thought to stem from exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis (EIMB) in skeletal muscle. The transcriptional coactivator PGC-1α, a potent regulator of metabolism in numerous tissues, is widely believed to be required for EIMB. We show here that this is not the case. Mice engineered to lack PGC-1α specifically in skeletal muscle (Myo-PGC-1αKO mice) retained intact EIMB. The exercise capacity of these mice was comparable to littermate controls. Induction of metabolic genes after 2 weeks of in-cage voluntary wheel running was intact. Electron microscopy revealed no gross abnormalities in mitochondria, and the mitochondrial biogenic response to endurance exercise was as robust in Myo-PGC-1αKO mice as in wildtype mice. The induction of enzymatic activity of the electron transport chain by exercise was likewise unperturbed in Myo-PGC-1αKO mice. These data demonstrate that PGC-1α is dispensable for exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle, in sharp contrast to the prevalent assumption in the field.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) deacetylase activity is not required for mitochondrial biogenesis or peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1alpha) deacetylation following endurance exercise.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 2;286(35):30561-30570. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.261685. Epub 2011 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21757760 Free PMC article.
-
PGC-1alpha plays a functional role in exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis and angiogenesis but not fiber-type transformation in mouse skeletal muscle.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Mar;298(3):C572-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00481.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 23. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20032509 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) deacetylation by physical activity: intact adipocytokine signaling is required.Diabetes. 2011 Jan;60(1):157-67. doi: 10.2337/db10-0331. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 20929977 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination of mitochondrial biogenesis by PGC-1α in human skeletal muscle: A re-evaluation.Metabolism. 2018 Feb;79:42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2017.11.001. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Metabolism. 2018. PMID: 29126696 Review.
-
PGC-1alpha regulation by exercise training and its influences on muscle function and insulin sensitivity.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Aug;299(2):E145-61. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00755.2009. Epub 2010 Apr 6. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20371735 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial network remodeling: an important feature of myogenesis and skeletal muscle regeneration.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 May;78(10):4653-4675. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03807-9. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33751143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis coincides with the expression of mitochondrial translation factors in murine skeletal muscle.Physiol Rep. 2018 Oct;6(20):e13893. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13893. Physiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30369085 Free PMC article.
-
Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α) in denervation-induced atrophy in aged muscle: facts and hypotheses.Longev Healthspan. 2013 Aug 1;2(1):13. doi: 10.1186/2046-2395-2-13. Longev Healthspan. 2013. PMID: 24472348 Free PMC article.
-
Mitofusion is required for MOTS-c induced GLUT4 translocation.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 12;11(1):14291. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93735-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34253808 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose triglyceride lipase deletion from adipocytes, but not skeletal myocytes, impairs acute exercise performance in mice.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015 May 15;308(10):E879-90. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00530.2014. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 25783895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gollnick PD, King DW. Effect of exercise and training on mitochondria of rat skeletal muscle. The American journal of physiology. 1969;216:1502–1509. - PubMed
-
- Freyssenet D, Berthon P, Denis C. Mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle in response to endurance exercises. Arch Physiol Biochem. 1996;104:129–141. - PubMed
-
- Little JP, Safdar A, Benton CR, Wright DC. Skeletal muscle and beyond: the role of exercise as a mediator of systemic mitochondrial biogenesis. Applied physiology, nutrition, and metabolism = Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme. 2011;36:598–607. - PubMed
-
- Ostergard T, Andersen JL, Nyholm B, Lund S, Nair KS, et al. Impact of exercise training on insulin sensitivity, physical fitness, and muscle oxidative capacity in first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetic patients. American journal of physiology Endocrinology and metabolism. 2006;290:E998–1005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

