Effects of exogenous cholecystokinin octapeptide on acquisition of naloxone precipitated withdrawal induced conditioned place aversion in rats
- PMID: 22848639
- PMCID: PMC3407117
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041860
Effects of exogenous cholecystokinin octapeptide on acquisition of naloxone precipitated withdrawal induced conditioned place aversion in rats
Abstract
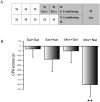
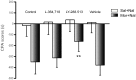
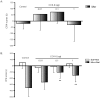
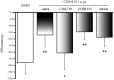
Cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8), a gut-brain peptide, regulates a variety of physiological behavioral processes. Previously, we reported that exogenous CCK-8 attenuated morphine-induced conditioned place preference, but the possible effects of CCK-8 on aversively motivated drug seeking remained unclear. To investigate the effects of endogenous and exogenous CCK on negative components of morphine withdrawal, we evaluated the effects of CCK receptor antagonists and CCK-8 on the naloxone-precipitated withdrawal-induced conditioned place aversion (CPA). The results showed that CCK2 receptor antagonist (LY-288,513, 10 µg, i.c.v.), but not CCK1 receptor antagonist (L-364,718, 10 µg, i.c.v.), inhibited the acquisition of CPA when given prior to naloxone (0.3 mg/kg) administration in morphine-dependent rats. Similarly, CCK-8 (0.1-1 µg, i.c.v.) significantly attenuated naloxone-precipitated withdrawal-induced CPA, and this inhibitory function was blocked by co-injection with L-364,718. Microinjection of L-364,718, LY-288,513 or CCK-8 to saline pretreated rats produced neither a conditioned preference nor aversion, and the induction of CPA by CCK-8 itself after morphine pretreatments was not significant. Our study identifies a different role of CCK1 and CCK2 receptors in negative affective components of morphine abstinence and an inhibitory effect of exogenous CCK-8 on naloxone-precipitated withdrawal-induced CPA via CCK1 receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Carlezon WA Jr (2003) Place conditioning to study drug reward and aversion. Methods Mol Med 84: 243–249. - PubMed
-
- Moran TH, Schwartz GJ (1994) Neurobiology of cholecystokinin. Crit Rev Neurobiol 9(1): 1–28. - PubMed
-
- Faris PL, Komisaruk BR, Watkins LR, Mayer DJ (1983) Evidence for the neuropeptide cholecystokinin as an antagonist of opiate analgesia. Science 219: 310–312. - PubMed
-
- Runkorg K, Veraksits A, Kurrikoff K, Luuk H, Raud S, et al. (2003) Distinct changes in the behavioural effects of morphine and naloxone in CCK2 receptor-deficient mice. Behav Brain Res 144 1–2: 125–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

