Treating inflammation by blocking interleukin-1 in a broad spectrum of diseases
- PMID: 22850787
- PMCID: PMC3644509
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd3800
Treating inflammation by blocking interleukin-1 in a broad spectrum of diseases
Abstract
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is a highly active pro-inflammatory cytokine that lowers pain thresholds and damages tissues. Monotherapy blocking IL-1 activity in autoinflammatory syndromes results in a rapid and sustained reduction in disease severity, including reversal of inflammation-mediated loss of sight, hearing and organ function. This approach can therefore be effective in treating common conditions such as post-infarction heart failure, and trials targeting a broad spectrum of new indications are underway. So far, three IL-1-targeted agents have been approved: the IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra, the soluble decoy receptor rilonacept and the neutralizing monoclonal anti-IL-1β antibody canakinumab. In addition, a monoclonal antibody directed against the IL-1 receptor and a neutralizing anti-IL-1α antibody are in clinical trials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
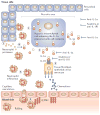


References
-
- Dinarello CA. Biological basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood. 1996;87:2095–2147. - PubMed
-
- Vojinovic J, et al. Safety and efficacy of an oral histone deacetylase inhibitor in systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:1452–1458. - PubMed
-
- Larsen CM, et al. Interleukin-1-receptor antagonist in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1517–1526. This study opens the door to the concept that type 2 diabetes is an inflammatory disease that is primarily mediated by IL-1β. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

