Social context induces two unique patterns of c-Fos expression in adolescent and adult rats
- PMID: 22851043
- PMCID: PMC3488116
- DOI: 10.1002/dev.21064
Social context induces two unique patterns of c-Fos expression in adolescent and adult rats
Abstract
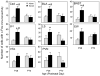
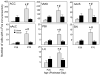
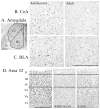
The study assessed possible age differences in brain activation patterns to low dose ethanol (.5 g/kg intraperitoneally) and the influence of social context on this activation. Early adolescent or young adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were placed either alone or with an unfamiliar partner of the same age and sex following saline or ethanol administration. c-Fos protein immunoreactivity was used to index neuronal activation in 15 regions of interest. Ethanol had little effect on c-Fos activation. In adolescents, social context activated an "autonomic" network including the basolateral and central amygdala, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, lateral hypothalamus, and lateral septum. In contrast, when adult rats were alone, activation was evident in a "reward" network that included the substantia nigra, nucleus accumbens, anterior cingulate and orbitofrontal cortices, lateral parabrachial nucleus, and locus coeruleus.
Keywords: adolescent; alcohol; autonomic system; immediate early genes; rat; reward system; social context.
© 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ethanol-induced Fos immunoreactivity in the extended amygdala and hypothalamus of the rat brain: focus on cholinergic interneurons of the nucleus accumbens.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2004 Apr;28(4):588-97. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000122765.58324.6d. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2004. PMID: 15100610
-
Fos activation patterns related to acute ethanol and conditioned taste aversion in adolescent and adult rats.Alcohol. 2019 Aug;78:57-68. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2019.02.004. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Alcohol. 2019. PMID: 30797833 Free PMC article.
-
Rewarding brain stimulation induces only sparse Fos-like immunoreactivity in dopaminergic neurons.Neuroscience. 1998 Mar;83(2):501-15. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(97)00409-0. Neuroscience. 1998. PMID: 9460758
-
Regional specificity of ethanol and NMDA action in brain revealed with FOS-like immunohistochemistry and differential routes of drug administration.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001 Nov;25(11):1662-72. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001. PMID: 11707641
-
Activation and desensitization of Fos immunoreactivity in the rat brain following ethanol administration.Brain Res. 1995 May 8;679(1):89-98. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(95)00210-h. Brain Res. 1995. PMID: 7648269
Cited by
-
Late aging alters behavioral sensitivity to ethanol in a sex-specific manner in Fischer 344 rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2018 Dec;175:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2018.07.012. Epub 2018 Aug 29. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2018. PMID: 30171932 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of c-Fos induction in response to social interaction in male and female Fisher 344 rats.Brain Res. 2017 Oct 1;1672:113-121. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.07.022. Epub 2017 Jul 29. Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 28764933 Free PMC article.
-
Social Interaction With an Alcohol-Intoxicated or Cocaine-Injected Peer Selectively Alters Social Behaviors and Drinking in Adolescent Male and Female Rats.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019 Dec;43(12):2525-2535. doi: 10.1111/acer.14208. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019. PMID: 31585020 Free PMC article.
-
Immediate early gene expression reveals interactions between social and nicotine rewards on brain activity in adolescent male rats.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Oct 15;313:244-254. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.07.024. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27435419 Free PMC article.
-
From adolescence to late aging: A comprehensive review of social behavior, alcohol, and neuroinflammation across the lifespan.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019;148:231-303. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 24. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31733665 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aggleton JP, Saunders RC. The amygdala - what’s happened in the last decade? In: Aggleton JP, editor. The Amygdala: A Functional Analysis. New York: Oxford University Press; 2001. pp. 1–30.
-
- Bardo MT, Dwoskin LP. Biological connection between novelty- and drug-seeking motivational systems. Motivational Factors in the Etiology of Drug Abuse. 2004;50:127–158. - PubMed
-
- Beck KH, Treiman KA. The relationship of social context of drinking, perceived social norms, and parental influence to various drinking patterns of adolescents. Addictive Behaviors. 1996;21(5):633–644. - PubMed
-
- Blakemore SJ. The social brain in adolescence. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2008;9(4):267–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

