Heat shock protein 90 inhibitors reduce trafficking of ATP-gated P2X1 receptors and human platelet responsiveness
- PMID: 22851178
- PMCID: PMC3463321
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.376566
Heat shock protein 90 inhibitors reduce trafficking of ATP-gated P2X1 receptors and human platelet responsiveness
Abstract
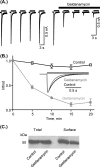
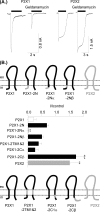
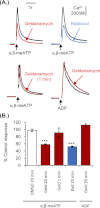
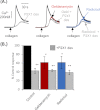
We have used selective inhibitors to determine whether the molecular chaperone heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) has an effect on both recombinant and native human P2X1 receptors. P2X1 receptor currents in HEK293 cells were reduced by ∼70-85% by the selective HSP90 inhibitor geldanamycin (2 μM, 20 min). This was associated with a speeding in the time course of desensitization as well as a reduction in cell surface expression. Imaging in real time of photoactivatable GFP-tagged P2X receptors showed that they are highly mobile. Geldanamycin almost abolished this movement for P2X1 receptors but had no effect on P2X2 receptor trafficking. P2X1/2 receptor chimeras showed that the intracellular N and C termini were involved in geldanamycin sensitivity. Geldanamycin also inhibited native P2X1 receptor-mediated responses. Platelet P2X1 receptors play an important role in hemostasis, contribute to amplification of signaling to a range of stimuli including collagen, and are novel targets for antithrombotic therapies. Platelet P2X1 receptor-, but not P2Y1 receptor-, mediated increases in intracellular calcium were reduced by 40-45% following HSP90 inhibition with geldanamycin or radicicol. Collagen stimulation leads to ATP release from platelets, and calcium increases to low doses of collagen were also reduced by ∼40% by the HSP90 inhibitors consistent with an effect on P2X1 receptors. These studies suggest that HSP90 inhibitors may be as effective as selective antagonists in regulating platelet P2X1 receptors, and their potential effects on hemostasis should be considered in clinical studies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ca2+ influx through P2X1 receptors amplifies P2Y1 receptor-evoked Ca2+ signaling and ADP-evoked platelet aggregation.Mol Pharmacol. 2014 Sep;86(3):243-51. doi: 10.1124/mol.114.092528. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Mol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24923466
-
Lipid raft association and cholesterol sensitivity of P2X1-4 receptors for ATP: chimeras and point mutants identify intracellular amino-terminal residues involved in lipid regulation of P2X1 receptors.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 22;285(43):32770-32777. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.148940. Epub 2010 Aug 10. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20699225 Free PMC article.
-
HSP90 inhibitors strengthen extracellular ATP-stimulated synthesis of interleukin-6 in osteoblasts: Amplification of p38 MAP kinase.Cell Biochem Funct. 2021 Jan;39(1):88-97. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3566. Epub 2020 Jun 21. Cell Biochem Funct. 2021. PMID: 32567086
-
[The role of purine receptors of thrombocytes in regulation of hemostasis].Klin Lab Diagn. 2012 Nov;(11):30-5. Klin Lab Diagn. 2012. PMID: 23305015 Review. Russian.
-
Geldanamycin, radicicol, and chimeric inhibitors of the Hsp90 N-terminal ATP binding site.Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6(11):1173-82. doi: 10.2174/156802606777812031. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16842154 Review.
Cited by
-
P2X4 receptor re-sensitization depends on a protonation/deprotonation cycle mediated by receptor internalization and recycling.J Physiol. 2018 Oct;596(20):4893-4907. doi: 10.1113/JP275448. Epub 2018 Sep 17. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30144063 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologic dissection of the overlapping impact of heat shock protein family members on platelet function.J Thromb Haemost. 2020 May;18(5):1197-1209. doi: 10.1111/jth.14758. Epub 2020 Mar 30. J Thromb Haemost. 2020. PMID: 32022992 Free PMC article.
-
ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD-95 multi-protein complex.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 19;6:33609. doi: 10.1038/srep33609. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27640997 Free PMC article.
-
Blood cells: an historical account of the roles of purinergic signalling.Purinergic Signal. 2015 Dec;11(4):411-34. doi: 10.1007/s11302-015-9462-7. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Purinergic Signal. 2015. PMID: 26260710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purinergic control of inflammation and thrombosis: Role of P2X1 receptors.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2014 Nov 28;13:106-10. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2014.11.008. eCollection 2015. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2014. PMID: 25709760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burnstock G. (2006) Pathophysiology and therapeutic potential of purinergic signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 58, 58–86 - PubMed
-
- Abbracchio M. P., Burnstock G. (1994) Purinoceptors: are there families of P2X and P2Y purinoceptors? Pharmacol. Ther. 64, 445–475 - PubMed
-
- North R. A. (2002) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol. Rev. 82, 1013–1067 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

